Depreciation is a charge on the business for use of a Fixed Asset. Business profits should be computed only after charging depreciation. The purpose of providing for depreciation is to retain funds in the business during its useful life so that it can be replaced at the end of life, without causing disruption to the business. However, separate Depreciation Reserves must be maintained if funds are to be actually available; the simple act of providing for depreciation does not.
The Depreciation tab for every fixed asset in CREST ERP lets you manage the process effectively.
Section 1 shows the summary info for the asset
Section 2 shows the method of depreciation chosen for the asset.
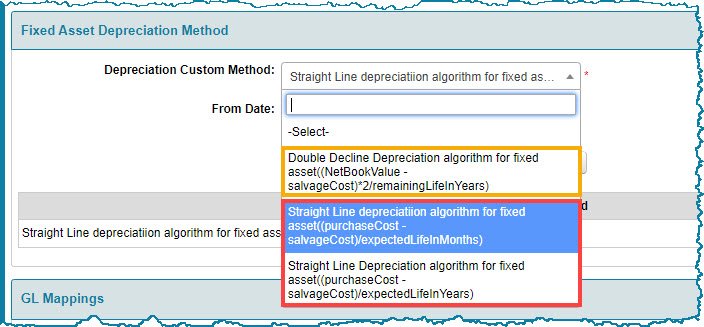
In the case of new assets, you must first set the Method of depreciation, for depreciation to be computed for the same. There are two main methods of depreciation, the Straight Line Method (SLM) and the Written Down Value (WDV) or Book Value method.
Under SLM, the cost of the asset, net of salvage value if any, is amortized over the useful life of the asset. Under WDV Method, higher depreciation is charged during the initial years. The method of depreciation is chosen based on the nature of the asset and the accounting policy of the business. SLM is chosen in the case of assets where there is no drastic decline in the performance or utility of the asset over its expected life.
CREST ERP supports both the methods, though under WDV, it supports only Double Declining Balance method (DDB), under which higher depreciation is charged during the initial years at the twice the SLM rate. It is also called ‘Accelerated depreciation’.
Section 3 shows the General Ledger accounts mapped for the asset for the Fixed Asset, Current Depreciation and Accumulated Depreciation accounts. These are based on the Fixed Asset Type GL Defaults under Organisation GL Settings > GL Account Defaults
Section 4 shows the depreciation charged for the asset for the historical periods


![Financials-GL-Depreciation tab [click to zoom] Financials-GL-Depreciation tab-CREST ERP](https://manula.r.sizr.io/large/user/18735/img/gl-073-fixed-asset-depreciation-tab-complete.jpg)
![Financials-GL-Depn. summary tab [click to zoom] Financials-GL-Depn. summary tab-CREST ERP](https://manula.r.sizr.io/large/user/18735/img/gl-073a-fixed-asset-depreciation-tab-history.jpg)
![Financials-GL-Depn tab-method [click to zoom] Financials-GL-Depn tab-method-CREST ERP](https://manula.r.sizr.io/large/user/18735/img/gl-073b-fixed-asset-depreciation-tab-method.jpg)
![Financials-GL-Fixed Assets-Depn tab-GL mappings [click to zoom] Financials-GL-Fixed Assets-Depn tab-GL mappings-CREST ERP](https://manula.r.sizr.io/large/user/18735/img/gl-073c-fixed-asset-depreciation-tab-gl-mappings.jpg)
![Financials-GL-Fixed assets-Depn tab-Depn report [click to zoom] Financials-GL-Fixed assets-Depn tab-Depn report [click to zoom]](https://manula.r.sizr.io/large/user/18735/img/gl-073d-fixed-asset-depreciation-tab-depn-report.jpg)

Post your comment on this topic.