The complete model, with all LIDs included, is in the file Example4.inp. It was simulated using Dynamic Wave flow routing with specific time steps for wet runoff, reporting, and routing. Figures 4-8 and 4-9 compare influent and effluent runoff for filter strip S_FS_1 and infiltration trench S_IT_1, while similar results are observed for other LIDs. Tables 4-12 and 4-13 list runoff coefficients for filter strips and infiltration trenches, representing the fraction of effluent-runoff volume to influent-runoff volume. The reduction in runoff volume provided by the LID can be calculated as 1 minus the runoff coefficient.

Figure 4-8

Figure 4-9
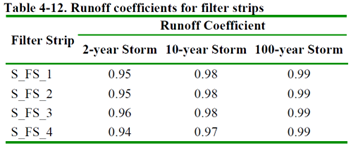
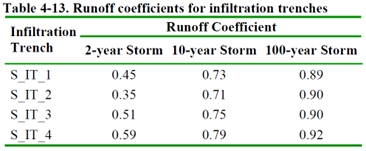
Filter strips hardly affect runoff control; they mainly remove pollutants and don’t manage flow rates or volumes. In contrast, all infiltration trenches substantially reduce runoff volume, especially during lighter rains. Notably, these trenches lack vegetation, which, if added, could impact their effectiveness depending on the design.



Figure 4-10

Figure 4-11


