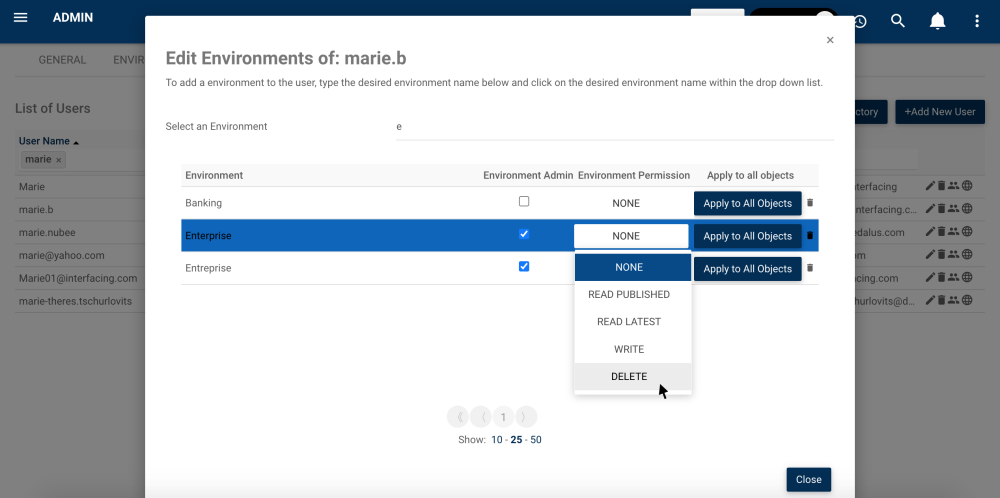
Admins and Modelers can access the Security button, assign and customize the security settings for EPC environments and/or objects, under these conditions:
- System Admins can define environment and object security permissions
- Environment Admins can define object security permissions
- Modelers with Delete permission can define object security permissions
The different levels of security that can be assigned to EPC objects are the following:
| Level of Security | Description |
|---|---|
| System Admin | User has all levels of permission on all objects of the system |
| Environment Admin | User has all levels of permission on all objects of an environment |
| Read published | User will be able to see only the published version of the object and won’t see “in progress” (draft) versions. Additionally, they won’t be able to edit or delete the object. |
| Read latest | User will be able to see all versions of the object but won’t be able to edit or delete it. |
| Write | User will have access to all versions of the object as well as editing rights but won’t be able to delete the object. |
| Delete | User will be able to see all versions of the object, edit it, delete it and if they are a modeler, they’ll be able to modify the security settings of the object. |
To learn more about process and flow object-specific permissions, please click here.
Direct Security: How it works
Users can define the security of groups or users by assigning them permissions on environments, sets, folders and objects, all independently or including their children objects, by clicking on the “Apply to children” or “Apply to all objects” box. If this box was not clicked before saving, the permission will not be inherited by children objects. The settings on children objects can be modified without affecting the settings of its parents.

As an example, you could grant “delete” on a set to a group, but only grant them “read latest” on a more delicate folder within that set, ensuring that nobody in the group will be able to edit or delete. This way of assigning security allows to set independent and micro-settings of security.
On the other hand, if your security needs are simpler, it is possible to set these permissions at the environment level. This way, you can grant permissions at once, for all objects in the environment by clicking on the “Apply to all objects” box.
How to set Security Permissions for an EPC Object
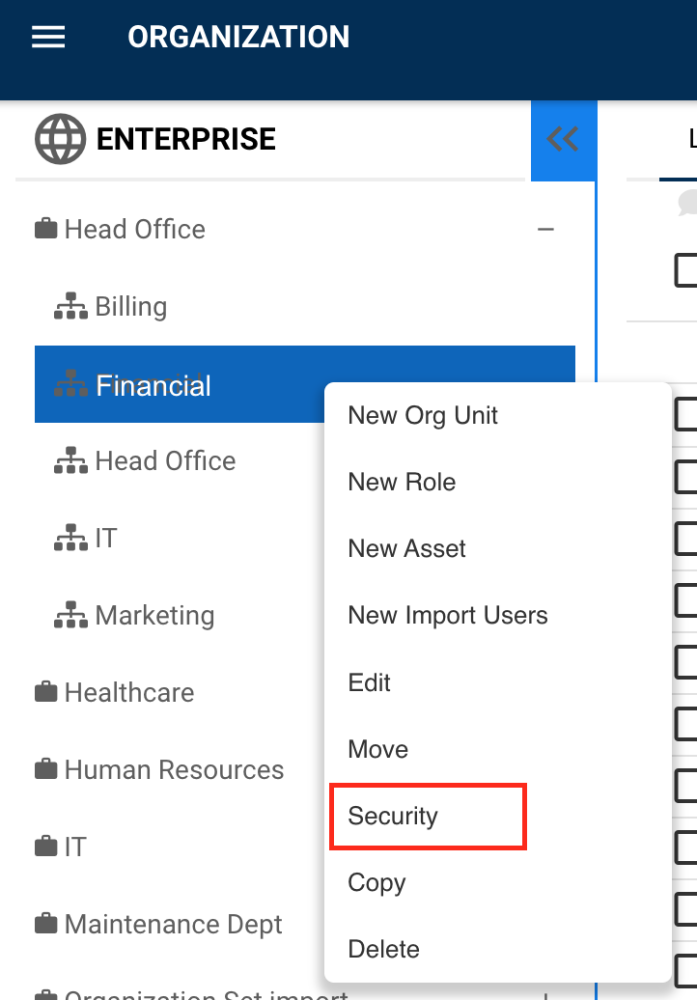
1. Navigate to the desired object in the hierarchy tree and right-click. Select the “Security” button. The security button can also be accessed in the Details page, under the “Edit” menu
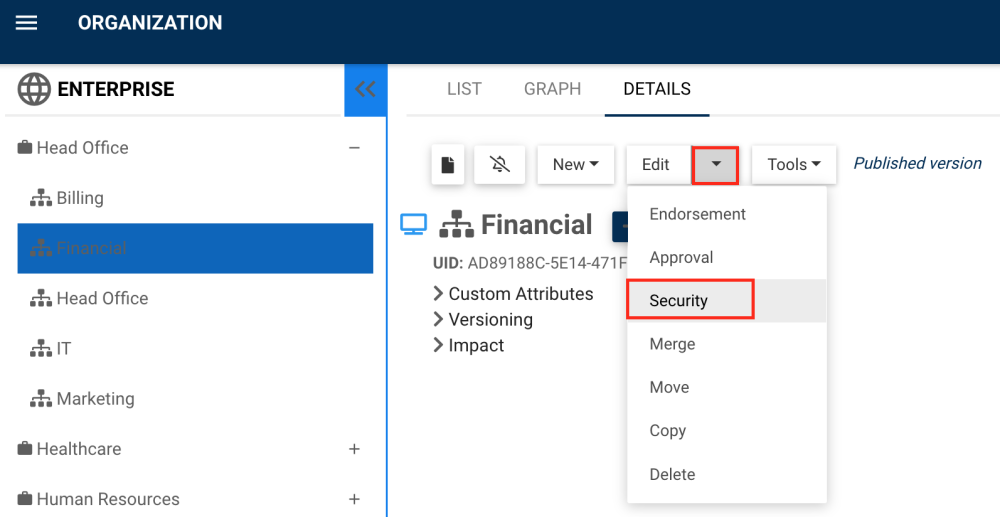
2. You will be redirected to the “Edit Security of: [Object] window.
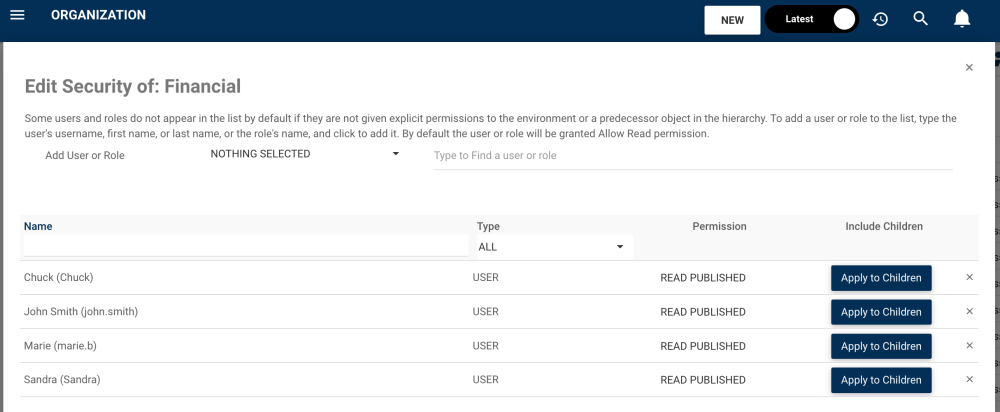
3. To add a user, role or group to the list, users can navigate to “Add User, Role or Group” and select a filter if desired.
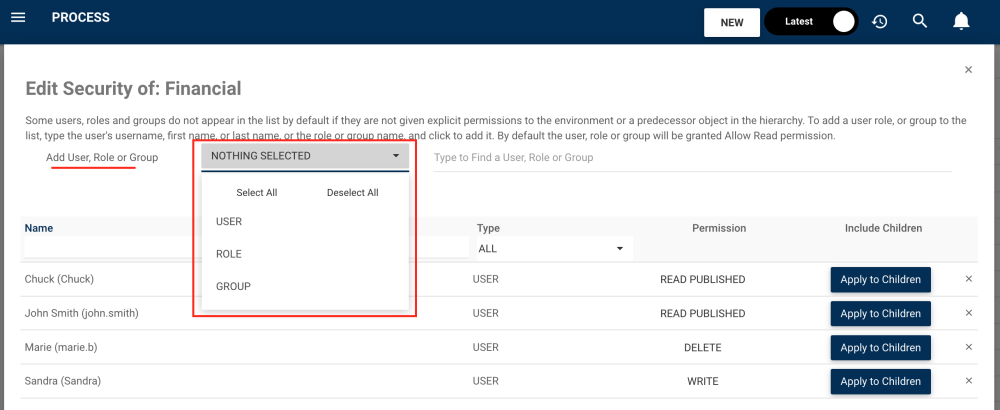
4. Here, we chose a role. Type the name of the Role you want to set a security permission for the EPC object. From the search suggestions, click to select the Role you want to assign
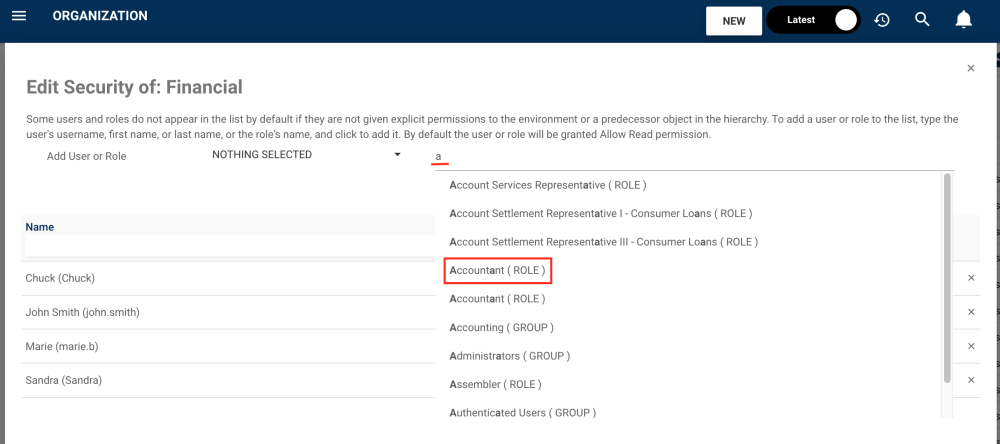
5. The Role will appear on the table under, where the security level can be assigned. By default, the user or role will be granted Read Published permission.
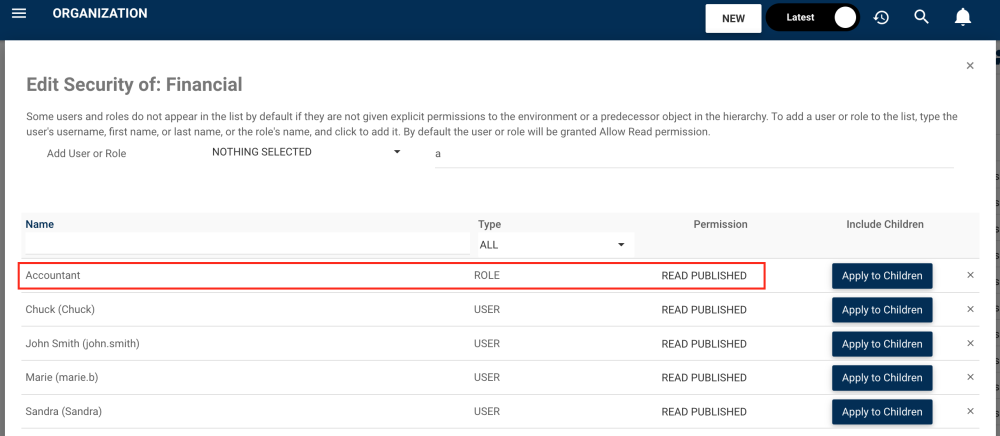
6. To change the default security setting, navigate to the Read Published permission box and click to open. Within the drop-down, select the desired permission.
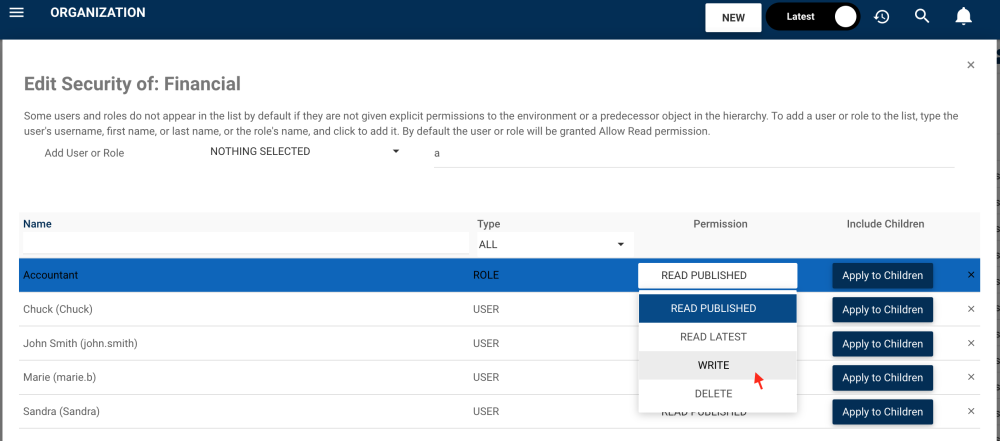
7. To remove the permission from the object, click on the “x”.
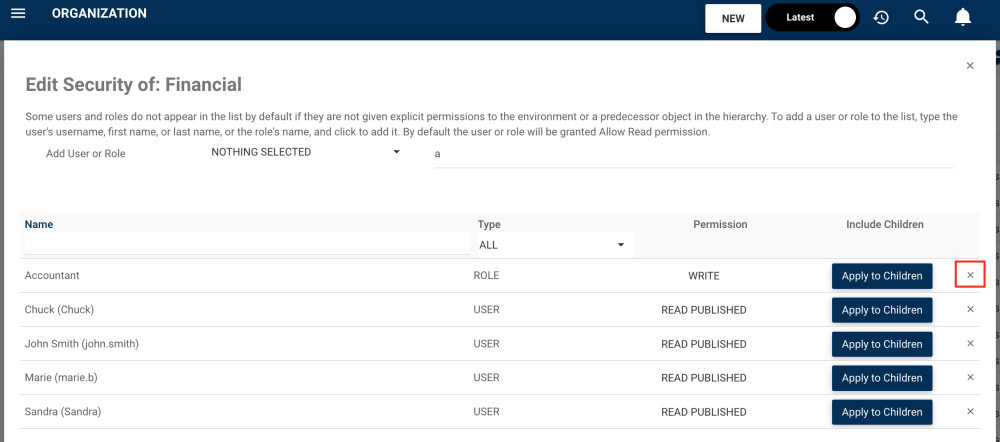
8. To propagate the permission to the all the children objects of the organization unit, select the “Apply to children” box.

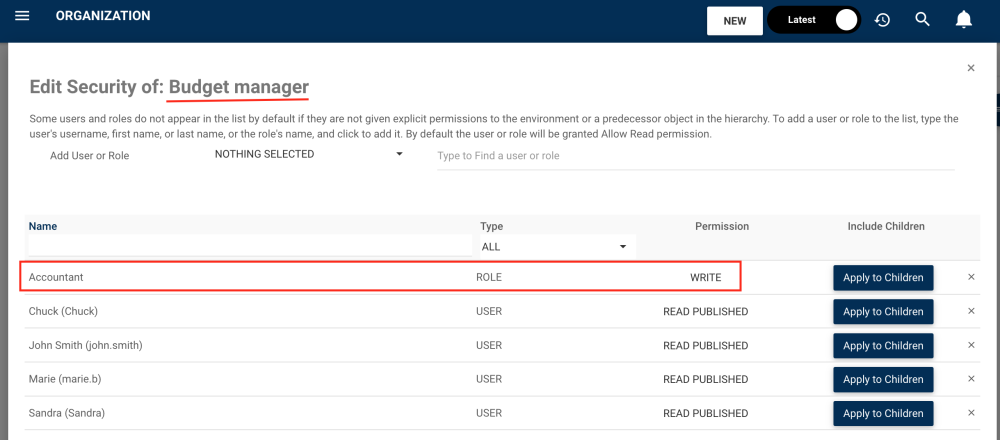
9. The permission will be applied to all children. Here’s an example of a Role within the Financial Org. Unit.
Additional Rules
What security will I have if I have two permissions on an object, one for my group and one for my user?
You will have the lowest security is the one granted. For example, if you have read latest permission on an object, but your group has delete permission on that same object, you will have read latest permission.
What will be the security of the object if I move it?
The object will be moved with its initial permissions.
What will be the default security of an object when I create it?
The object will inherit the permissions of its parent. For example, if we create a document set and a user has “Delete” permission on the environment (the environment is the parent of sets), then the user will have default “Delete” permission on the set, unless manually changed.
What will be the security of the object if I merge it?
The object will have the security of the object you are merging it to.
What will be the security of the object if I copy it?
The copied object will inherit permission from the parent object where you want the copy. For example, if you copy an object and place it in a folder for which you have “Write” permission, the object will have the same permission. Same applies for the Create Records function.
Locked Objects
For all Modules, updating the security on an object that is being edited is not prevented. The user won’t receive a lock error message.
Need more help with this?
Visit the Support Portal