Hodgkin lymphoma (HL or Hodgkin disease) is a cancer of the immune system that is marked by the presence of a type of cell called the Reed-Sternberg cell. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classical Hodgkin lymphoma (90-95% of cases) and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma (5-10% of cases).
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma can be further subdivided into four histologic subtypes: nodular sclerosis (NS), mixed cellularity (MC), lymphocyte deplete (LD), and lymphocyte rich (LR). Symptoms include the painless enlargement of lymph nodes, spleen, or other immune tissue. Generalized pruritus is also common and may precede the diagnosis by months. The most common sites of involvement include cervical, supraclavicular, and mediastinal lymph nodes. Central nervous system involvement may occur in rare cases. Other symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, and/or night sweats.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is a large group of cancers derived from lymphocytes (white blood cells). Non-Hodgkin lymphomas can occur at any age and are often marked by enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. There are many different types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These types can be divided into aggressive (fast-growing), intermediate, or indolent (slow-growing), and can develop from either
B-cells or T-cells.
Lymphomas that occur after allogeneic bone marrow or stem cell transplantation are usually B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas and are collectively known as post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLD).
Table 1. How does HL differ from NHL?
| HL | NHL | |
|---|---|---|
| Subtypes | 2 | >30 |
| Peak Age | 20s | Over age 60 |
| Cases/year | 8,000 | 60,000 |
| Common Sites | Neck, mediastinum | Various |
| Severity of Symptoms | Usually mild | Often severe |
| 5-Year Survival Rate | > 80% | Varies |
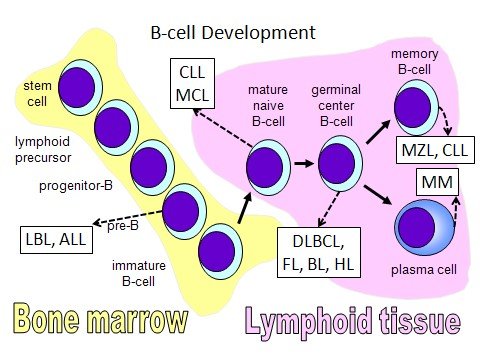
Graphic 1 shows the development of B-cells from stem cells in the bone marrow to memory B-cells and plasma cells in the lymphoid tissue. Neoplasms may develop at different points during B-cell development, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma from germinal center B-cells or mantle cell lymphoma from memory B-cells.
Graphic 1. B-cell Development.
Lymphoma Response Criteria
2018: LYM Pre-HCT
2118: LYM Post-HCT
Need more help with this?
Don’t hesitate to contact us here.