This section provides an overview of reporting chronic GVHD on the Post-TED (2450) and Post-Infusion Follow-Up (2100) Forms.
Development vs Persistence of Chronic GVHD
This section is intended to provide guidance on when to report Yes or No for questions asking if chronic GVHD developed or persisted.
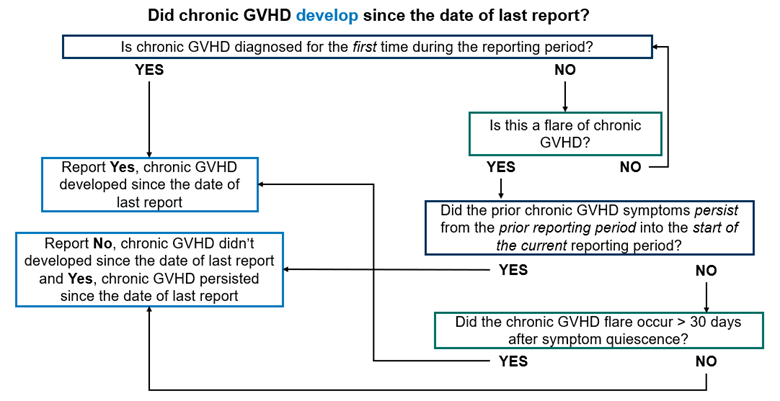
Did chronic GVHD develop since the date of last report should be answered as Yes in the following scenarios:
- Chronic GVHD was diagnosed for the first time during the reporting period.
- A chronic GVHD flare was diagnosed during the current reporting period and all the following conditions are met:
- The prior chronic GVHD symptoms did not persist from the prior reporting period into the beginning of the current reporting period.
- The flare was diagnosed after at least 30 days without any active chronic GVHD symptoms.
- Acute GVHD followed by chronic GVHD was previously diagnosed and resolved, a flare of acute GVHD was diagnosed in the current reporting period, and all the following conditions are met:
- The prior GVHD symptoms (acute and / or chronic) did not persist from the prior reporting period into the beginning of the current reporting period.
- The flare was diagnosed after at least 30 days without any active GVHD symptoms (acute and / or chronic).
Did chronic GVHD develop since the date of last report should be answered as No in the following scenarios:
- There were no active chronic GVHD symptoms during the current reporting period.
- Chronic GVHD symptoms were present in reporting the period, but they continued from the previous reporting period into the current reporting period.
- Acute GVHD followed by chronic GVHD was diagnosed in a prior reporting period and acute GVHD symptoms persisted into the current reporting period.
The Unknown option should only be used when there is no information about the recipient’s GVHD status for the entire reporting period. This option should be used sparingly and only when no judgement can be made about the presence or absence of GVHD in the reporting period.
Did chronic GVHD persist since the date of last report should be answered as Yes in the following scenarios:
- Chronic GVHD was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and the chronic GVHD symptoms have been active since diagnosis and continue to be active in the current reporting period (i.e., there is no period of symptom resolution or quiescence since diagnosis).
- Chronic GVHD symptoms resolved before the first day of the current reporting period, but a flare occurred within 30 days of symptom resolution / quiescence.
- Acute GVHD followed by chronic GVHD was previously diagnosed and resolved, a flare of acute GVHD was diagnosed in the current reporting period, and one of the following conditions are met:
- The prior GVHD symptoms (acute and / or chronic) persisted from the prior reporting period into the beginning of the current reporting period.
- The flare was diagnosed 30 days or less after symptom resolution.
Did chronic GVHD persist since the date of last report should be answered as No in the following scenarios:
- There were no active chronic GVHD symptoms during the current reporting period.
- Acute GVHD followed by chronic GVHD was previously diagnosed and resolved, a flare of acute GVHD was diagnosed in the current reporting period, and all the following conditions are met:
- The prior GVHD symptoms (acute and / or chronic) did not persist from the prior reporting period into the beginning of the current reporting period.
- The flare was diagnosed after at least 30 days without any active GVHD symptoms (acute and / or chronic).
The Unknown option should only be used when there is no information about the recipient’s GVHD status for the entire reporting period. This option should be used sparingly and only when no judgement can be made about the presence or absence of GVHD in the reporting period.
Chronic GVHD Grading, Organ Scoring, and Extent Criteria
When chronic is reported, the organ scoring at diagnosis is collected on the Post-Infusion Follow-Up (2100) Form and the maximum overall grade and extent in the reporting period is captured on both the Post-TED (2450) and Post-Infusion Follow-Up (2100) Forms.
Chronic GVHD Maximum Grade
The maximum chronic GVHD involvement, based on the opinion of the clinician (i.e., clinical grade) in the current reporting period is captured. The intent of this question is to capture the maximum grade based on the best clinical judgment. When both the global severity score and the score based on the clinician’s opinion is documented, report the clinician score. If the clinician score is not documented, seek physician documentation.
Guidelines on how to report the maximum grade of chronic GVHD are outlined below:
- Mild: Signs and symptoms of chronic GVHD do not interfere substantially with function and do not progress once appropriately treated with local therapy or standard systemic therapy (i.e., corticosteroids and / or cyclosporine or tacrolimus).
- Moderate: Signs and symptoms of chronic GVHD interfere somewhat with function despite appropriate therapy or are progressive through first line of systemic therapy (i.e., corticosteroids and / or cyclosporine or tacrolimus).
- Severe: Signs and symptoms of chronic GVHD limit function substantially despite appropriate therapy or are progressive through second line of therapy.
The Unknown option should only be used when there is no information about the recipient’s GVHD status for the entire reporting period. This option should be used sparingly and only when no judgment can be made about the status of the recipient’s GVHD.
In addition to reporting the maximum grade in the reporting period, the date when the maximum grade occurred is captured:
- Report the first date when the maximum grade occurred.
- When there are multiple instances when the same maximum grade occurred, report the earliest date.
Chronic GVHD Organ Scoring (At Diagnosis)
In addition to capturing the maximum grade, the organ involvement and NIH score of each organ involved at diagnosis of chronic GVHD is also collected. For each organ involvement, specific features present at diagnosis are also reported. Refer to the Organ Scoring of Chronic GVHD Table below for the NIH Consensus Criteria 2014 for organ scoring of chronic GVHD.
Organ Scoring of Chronic GVHD Table
| Organ | Score 0 | Score 1 | Score 2 | Score 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin %BSA1 | No BSA involved | 1-18% BSA | 19-50% BSA | >50% BSA |
| Skin Features | No sclerotic features | N/A | Superficial sclerotic features, but not “hidebound” | Deep sclerotic features; “hidebound;” impaired mobility; ulceration |
| Mouth | No symptoms | Mild symptoms with disease signs but not limiting oral intake significantly | Moderate symptoms with disease signs with partial limitation of oral intake | Severe symptoms with disease signs with major limitation of oral intake |
| Eyes | No symptoms | Mild dry eye symptoms not affecting ADL (requirement of lubricant drops ≤ 3x/day) | Moderate dry eye symptoms partially affecting ADL (requiring lubricant drops > 3x/day or punctal plugs) WITHOUT new vision impairment due to keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS) | Severe dry eye symptoms significantly affecting ADL (special eyewear to relieve pain) OR unable to work because of ocular symptoms OR loss of vision due to keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS) |
| GI Tract | No symptoms | Symptoms without significant weight loss (< 5%) | Symptoms associated with mild to moderate weight loss (5-15%) within 3 months OR moderate diarrhea without significant interference with daily living | Symptoms associated with significant weight loss (> 15%) within 3 months, requires nutritional supplement for most calorie needs OR esophageal dilation OR severe diarrhea with significant interference with daily living. |
| Liver | Normal total bilirubin and ALT or AP < 3 x ULN | Normal total bilirubin with ALT ≥ 3 to 5 x ULN or AP ≥ 3 ULN | Elevated total bilirubin but ≤ 3 mg / dL or ALT >5 x ULN | Elevated total bilirubin > 3 mg / dL |
| Lungs Symptom score: |
No symptoms | Mild symptoms (SOB after climbing one flight of steps) | Moderate symptoms (SOB after walking on flat ground) | Severe symptoms (SOB at rests; requires O2) |
| Lungs Lung score: |
FEV1 ≥ 80% | FEV1 60-79% | FEV1 40-59% | FEV1 ≤ 39% |
| Joints and Fascia | No symptoms | Mild tightness of arms or legs, normal or mild decreased range of motion AND not affecting ADL | Tightness of arms or legs OR joint contractures, erythema thought to be due to fasciitis, moderate decrease of range of motion AND mild to moderate limitation of ADL | Contractures WITH significant decrease of range of motion AND significant limitation of ADL (unable to tie shoes, button shirts, dress self, etc.) |
| Genital Tract2 | No signs | Mild signs and females with or without discomfort on exam | Moderate signs and may have signs of discomfort on exam | Severe signs with or without symptoms |
| Other Features3 | No GVHD | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
| NIH Consensus Criteria, 2014 1. Features to be scored by BSA: Maculopapular rash, lichen planus-like features, sclerotic features, papulosquamous lesions or ichthyosis, keratosis pilaris-like GVHD. 2. Scoring is based on severity of the signs instead of symptoms, based on limited available data and the opinions of experts. Female or male genital GVHD is not scored if a practitioner is unable to examine the patient. 3. May include ascites, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion(s), nephrotic syndrome, myasthenia gravis, peripheral neuropathy, polymyositis, weight loss without GI symptoms, eosinophilia > 500/μL, platelets < 100,000/μL, others. |
||||
Skin: Ranges from skin discoloration to severe scarring and tightness. Includes, but not limited to:
- Sclerosis: thickening of the skin, which may cause loss of suppleness
- Maculopapular rash / erythema: reddish skin with small confluent bumps / redness
- Lichen planus-like features: erythematous / violaceous flat-topped papules or plaques with or without surface reticulations or a silvery or shiny appearance.
- Papulosquamous lesions or ichthyosis: dry, scaly, or thickened skin
- Keratosis pilaris: small acne-like bumps and rough patches
- Poikiloderma: atrophy, pigmentary changes, and telangiectasia
In addition to reporting the NIH score BSA involved, the skin features score and the skin GVHD features present at diagnosis is reported. If any skin abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Mouth: Refers to white plaques, scarring, and ulcers occurring in the mouth and throat.
- Lichen planus-like features: whitish lacy patches that usually appear first on inner cheeks, but can involve roof of mouths, gums, and / or tongue.
If any mouth abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Eyes: Dry eyes and / or corneal ulcers due to keratoconjunctivitis sicca.
- Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS): dry eye syndrome
If any eye abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Gastrointestinal Tract (GI): Includes the following:
- Esophageal web / proximal stricture or ring: extension of esophageal tissue
- Dysphagia: difficulty swallowing
- Anorexia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss: weight loss ≥ 5%
- Failure to thrive
If any GI abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Liver: Include all types of liver abnormalities, either clinical or histological. Liver involvement may be manifested by elevation of liver function tests. Three are considered in the scoring system: total bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase; SGPT (ALT).
If any liver abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Lung: Ranges from mild impairment on pulmonary function tests to severe disorder. If a pulmonary function test was completed, the FEV1 percent from the diagnosis of chronic GVHD is reported.
If any lung abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Joints and Fascia: Includes the following:
- Contractures: loss of joint mobility due to skin or fascia changes
If any joint or fascia abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Genital Tract: Includes the following:
- Female: Vaginitis / stricture: pain, ulceration, inflammation, eventually scarring / narrowing of the vaginal opening.
- Male: Pain, burning sensation, lichen planus or lichen sclerosis features, scarring, stenosis.
The recipient’s sexually active status will be captured if the genital tract was involved at the diagnosis of chronic GVHD.
If any genital tract abnormalities were present, but explained entirely by non-GVHD causes, the documented causes are specified.
Chronic GVHD Extent
Another grading system for chronic GVHD is divided into two categories, limited and extensive. Definitions of limited and extensive are based on Sullivan KM, Blood 1981; 57:267. The intent of this data field is to capture if chronic GVHD was limited or extensive throughout the entire reporting period and is not dependent on the maximum grade and date of chronic GVHD. If the criteria to report extensive was met at any time in the current reporting period, Extensive should be reported. Use the guidelines below to determine how to report the extent.
- Limited: Localized skin involvement and / or liver dysfunction attributed to chronic GVHD.
- Extensive: Includes any of the following symptoms attributed to chronic GVHD:
- Generalized skin involvement and / or liver dysfunction.
- Liver histology showing chronic aggressive hepatitis, bridging necrosis, or cirrhosis.
- Involvement of the eye: Schirmer’s test with < 5 mm wetting.
- Involvement of minor salivary glands or oral mucosa demonstrated on labial biopsy (labial biopsy not required).
- Involvement of any other target organ.
Section Updates:
| Question Number | Date of Change | Add/Remove/Modify | Description | Reasoning (If applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| . | . | . | . |
Need more help with this?
Don’t hesitate to contact us here.

