Pulmonary Function
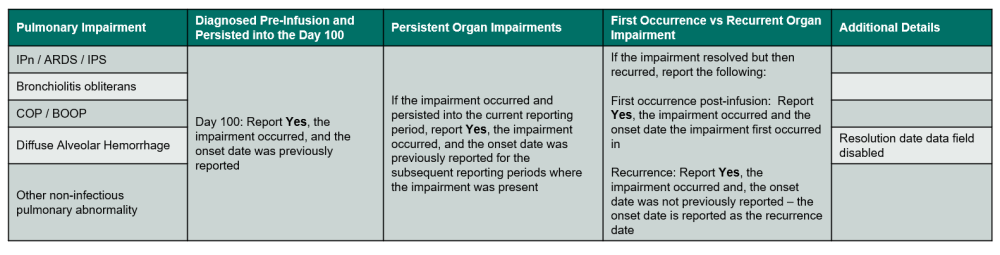
Table 1. Pulmonary Impairments
Questions 250 – 254: Did the recipient develop non-infectious interstitial pneumonitis (IPn or ARDS) / idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS)? (Report infectious pneumonia in infection section)
IPn refers to inflammation of the alveolar walls. Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) typically refers to fluid build-up within the alveoli. In either case, gas exchange is impaired resulting in oxygen deprivation. Both conditions can result from infectious or non-infectious causes.
Idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS) refers to all non-infectious lung injuries that occur early after HCT (within 100-120 days) including: peri-engraftment respiratory distress syndrome (PERDS), interstitial pneumonitis without a pathogen, radiation / drug-induced lung injury, or transfusion-associated lung injury (TRALI).
See below for common methods of assessment.
Indicate if non-infectious interstitial pneumonitis (IPn or ARDS) / idiopathic pneumonia syndrome (IPS) occurred in the current reporting period. If Yes, report the diagnosis date and the diagnostic method(s), other than radiographic studies. Select all that apply. Refer to Table 1. Pulmonary Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment.
Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period and did not recur in the current reporting period
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the diagnosis was determined at an outside center and no documentation of a clinical, pathological, or laboratory assessment is available, the dictated date of diagnosis within a physician note may be reported.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Documentation of diagnostic tests may be attached to the form. For further instructions on how to attach documents in FormsNet3, refer to the FormsNet3 Training Guide.
Diagnostic Methods:
- Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL): a procedure in which a bronchoscope is guided into the lower respiratory system. Fluid is emitted from the bronchoscope and then collected for further examination.
- Transbronchial biopsy: a procedure in which forceps on the end of the bronchoscope are used to collect lung tissue samples for further examination.
- Open / thorascopic lung biopsy: An open lung biopsy is a procedure in which an incision is made between the ribs to collect a sample of lung tissue for further examination. A thorascopic lung biopsy is a procedure in which an incision is made to the chest and an endoscope is used to collect samples of lung tissue.
- Autopsy: a post-mortem procedure used to determine the cause of death and to evaluate other disease present at the time of death.
- Other diagnostic test: If a diagnostic test, other than radiographic studies was performed, specify the test.
- No diagnostic tests done: If no diagnostic tests (other than radiographic studies) were performed, select this option.
Questions 255 – 256: Did IPn or ARDS / IPS resolve?
Indicate if IPn or ARDS / IPS resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. The resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed.
Questions 257 – 263: Specify other non-infectious pulmonary abnormality developed (e.g. bronchiolitis obliterans, COP / BOOP, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage)
Indicate if any other non-infectious pulmonary abnormality (listed below) occurred in the current reporting period. If the impairment occurred, report the diagnosis date and the diagnostic method(s), other than radiographic studies. Select all that apply. Refer to Table 1. Pulmonary Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment.
Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the recipient did not develop any other non-infectious pulmonary abnormality, select None.
Other Non-Infectious Pulmonary Abnormalities
- Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO): an airway obstruction as a result of inflammation of the bronchioles. This complication typically occurs late after HCT. It is often a manifestation of chronic GVHD. If bronchiolitis obliterans is a result of chronic GVHD, confirm that bronchiolitis obliterans was also reported in the chronic GVHD section of this form.
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP) / Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (BOOP): an idiopathic form of pneumonia which affects different parts of the lungs including the bronchioles and alveoli. This complication typically occurs late after HCT.
- Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH): bleeding into the alveolar space typically resulting from an injury to the pulmonary blood vessels.
- Other non-infectious pulmonary abnormality: any other non-infectious pulmonary abnormalities not already captured in the above categories. Do not report pleural effusions here.
If the diagnosis was determined at an outside center and no documentation of a clinical, pathological, or laboratory assessment is available, the dictated date of diagnosis within a physician note may be reported.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Diagnostic Methods:
- Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL): a procedure in which a bronchoscope is guided into the lower respiratory system. Fluid is emitted from the bronchoscope and then collected for further examination.
- Transbronchial biopsy: a procedure in which forceps on the end of the bronchoscope are used to collect lung tissue samples for further examination.
- Open / thorascopic lung biopsy: An open lung biopsy is a procedure in which an incision is made between the ribs to collect a sample of lung tissue for further examination. A thorascopic lung biopsy is a procedure in which an incision is made to the chest and an endoscope is used to collect samples of lung tissue.
- Autopsy: a post-mortem procedure used to determine the cause of death and to evaluate other disease present at the time of death.
- Other diagnostic test: If a diagnostic test, other than radiographic studies was performed, specify the test.
- No diagnostic tests done: If no diagnostic tests (other than radiographic studies) were performed, select this option.
Documentation of diagnostic tests may be attached to the form. For further instructions on how to attach documents in FormsNet3, refer to the FormsNet3 Training Guide.
Questions 264 – 265: Did non-infectious pulmonary abnormalities resolve?
Indicate if non-infectious pulmonary abnormalities resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. The resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed.
This question is disabled for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage.
Question 266 – 267: Did the recipient receive endotracheal intubation or mechanical ventilation?
Endotracheal intubation or mechanical ventilation may be used for respiratory failure or for airway protection from severe mucositis.
Invasive positive pressure ventilation is delivered via an endotracheal tube. Do not include non-invasive positive pressure ventilation that is delivered through an alternate interface (e.g., facemask).
Indicate whether the recipient received endotracheal intubation or mechanical ventilation (invasive positive pressure ventilation) post-HCT. If Yes, report the date when endotracheal intubation or mechanical ventilation was started. If the recipient was intubated multiple times within the reporting period, report the first date of intubation. Report No if the patient received endotracheal intubation or mechanical ventilation during surgery.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Question 268 – 269: Was the recipient successfully extubated?
Indicate if the recipient was successfully extubated during the reporting period. If Yes, report the date of extubation. If the recipient was extubated multiple times within the reporting period, please report the last date of extubation.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Liver Toxicity Function
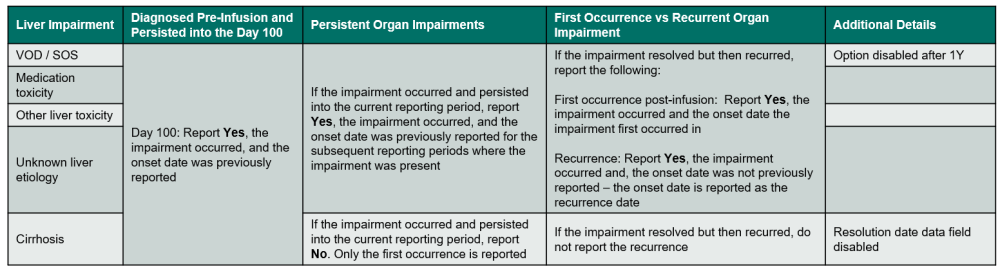
Table 2. Liver Impairments
Questions 270 – 271: Specify therapy used to prevent liver toxicity (check all that apply)
Liver toxicities in transplant patients may be related to drugs / treatments, infection, GVHD, iron overload, cirrhosis, or sinusoidal obstructive syndrome (SOS) / veno-occlusive disease (VOD). Agents such as ursodiol may be given as prophylaxis against one or more of these transplant-related liver injuries. Agents given to prevent liver toxicity will generally be started prior to or during the conditioning regimen and may be continued well after transplant.
Select all therapy the recipient received intended to prevent liver toxicity during the reporting period, including therapy given during the preparative regimen. Report only agents given to prevent liver toxicities, not those given to treat a diagnosed liver injury or toxicity.
Question 272 – 274: Did the recipient develop non-infectious liver toxicity (excluding GVHD)?
Indicate if a non-infectious liver toxicity occurred during the reporting period. Include toxicities which developed between the start of the preparative regimen and the date of last contact (question 1) when completing the 100-day follow-up form. Refer to Table 2. Liver Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment. Do not report liver complications due to GVHD in this section.
If the non-infectious toxicity is VOD / SOS, medication toxicity, other toxicity, and unknown etiology, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the non-infectious toxicity is cirrhosis, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion or in a previous reporting period and the impairment recurred post-infusion.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Question 275 – 278: Specify the etiology of the non-infectious liver toxicity etiology
Report the etiology of the non-infectious liver toxicity occurring in the reporting period and specify when the toxicity resolved. The resolution data field is disabled if the etiology is cirrhosis.
Non-Infectious Liver Toxicity Etiologies
- Veno-occlusive disease (VOD) / sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS): occurs following injury to the hepatic venous endothelium, resulting in hepatic venous outflow obstruction due to occlusion of the hepatic venules and sinusoids. This typically results in a distinctive triad of clinical signs including hepatomegaly with right upper quadrant tenderness, third space fluid retention (e.g., ascites), and jaundice with a cholestatic picture. For more information on VOD / SOS including diagnostic criteria, refer to the VOD / SOS section of the Forms Instructions Manual.
- Cirrhosis: Cirrhosis is a degenerative disease in which fibrous tissue forms and the lobes become filled with fat. Cirrhosis may be diagnosed using a liver biopsy, but clinical symptoms (enlarged liver), blood tests, laparoscopy, or radiology imaging are often used to determine the diagnosis of cirrhosis when a liver biopsy is not necessary. The resolution date data field is disabled for this option.
- Medication toxicity: If the liver abnormality (i.e., abnormal LFT values) is associated with drug initiation, abnormalities improve with cessation, and / or there are no other causes for the change.
- Other etiology: Liver toxicity other than VOD / SOS or cirrhosis. Do not include hepatic infections or GVHD.
- Unknown etiology: If there is a liver toxicity; however, there is no information about the etiology of the non-infectious liver toxicity. This option should be used sparingly and only when no judgment can be made about the etiology in the reporting period.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Thrombotic Microangiopathy (TMA)
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a multifactorial condition where intravascular platelet activation, formation of thrombi, and microangiopathic hemolytic anemia occur due to generalized endothelial dysfunction. Organ injury, specifically the kidney, may occur as a result of these processes.1 Characteristics of thrombotic microangiopathy includes microangiopathic hemolysis, thrombocytopenia (< 50 ×109/L), neurological changes, and pulmonary dysfunction: Other laboratory features include:
- LDH greater than the center-specific upper limit of normal
- Serum creatinine > 2 mg/dL or >50% rise over baseline
- Bilirubin greater than twice the center-specific upper limit of normal
1 Jodele, S., M. Davies, and B.L. Laskin. “Diagnostic and Risk Criteria for HSCT-associated Thrombotic Microangiopathy: A Study in Children and Young Adults.” Blood 124.4 (2014): 645-53. Web.
Table 3. TMA or Other Similar Syndromes
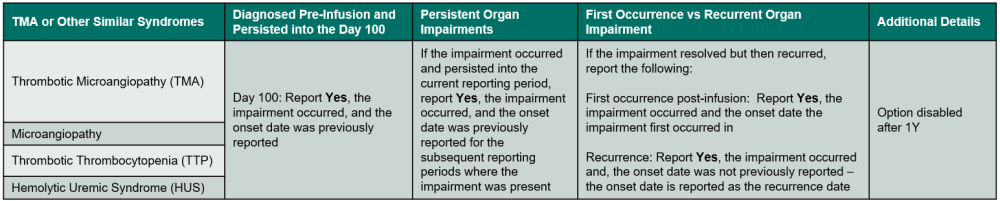
Questions 279 – 281: Did the recipient develop post-infusion thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) or similar syndrome? (includes microangiopathy, thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP), hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS))
Indicate if TMA or a similar syndrome occurred in the current reporting period. Refer to Table 3. TMA or Other Similar Syndromes for an overview of when to report the impairment.
Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
TMA or Similar Syndromes
- Microangiopathy: Disease of the capillaries where the capillaries bleed and slow the flow of blood due to thickening and weakening of capillary walls.
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenia (TTP): Blood disorder where blood clots form in the small blood vessels of the body.
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS): Abnormal destruction of red blood cells which block the kidneys resulting in kidney failure. May be caused by Escherichia coli, other infections, and medications.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Question 282: Specify signs and symptoms (check all that apply)
Report all TMA or a similar syndrome signs or symptoms the recipient experienced in the current reporting period. Select all that apply.
Questions 283 – 287: Was TMA evaluated by biopsy?
Indicate whether TMA was evaluated by a biopsy in the current reporting period.
If Yes, report if the results as Positive, Suggestive, Negative, Inconclusive / equivocal, or Not done. If Other site is reported, specify the biopsy site.
Indicate whether documentation was submitted to the CIBMTR (e.g., pathology report). For further instructions on how to attach documents in FormsNet3, refer to the FormsNet3 Training Guide.
Questions 288 – 289: Was therapy given for TMA?
Specify any therapy given in the current reporting period for TMA. Report only agents given to treat a diagnosis of TMA. If no therapy was given, select None.
Questions 290 – 291: Did the TMA resolve? (Normalization of renal function, LDH, and resolution or improvement in renal and / or neurologic dysfunction)
Indicate whether TMA resolved. If Yes, report the first date the recipient met the following criteria:
- Normalization of renal function (per institutional guidelines);
- Normalization of LDH (per institutional guidelines);
- Resolution / improvement of renal and neurologic dysfunction.
Other Organ Impairment / Disorder
The intent of this section is to identify serious conditions or impairments occurring after transplant. For the purposes of this manual, the term “clinically significant” refers to conditions requiring treatment or intervention. Additional guidelines for commonly reported organ impairments and disorders are included below. Do not report complications that are expected for most transplant recipients and do not require treatment (i.e., minor complications resolving without intervention).
Report any other clinically significant organ impairment or disorder occurring during the reporting period. Refer to the organ specific instructions below for further guidance. If this form is being completed for the 100-day reporting period, include any clinically significant impairments or disorders diagnosed between the start of the preparative regimen and the date of contact (question 1).
Table 4. Renal Impairments
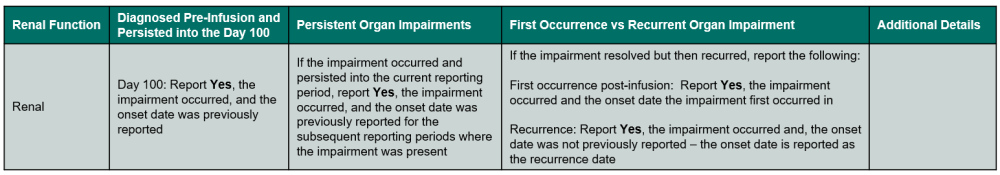
Questions 292 – 294: Did the recipient experience a renal impairment / disorder
Indicate if a renal impairment or disorder (stage 2 or 3 acute kidney failure and/or chronic kidney failure) occurred in the current reporting period. Refer to Table 4. Renal Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment.
Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the diagnosis was determined at an outside center and no documentation of a clinical, pathological, or laboratory assessment is available, the dictated date of diagnosis within a physician note may be reported.
Do not report stage 1 acute kidney failure or organ impairments / disorders.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Questions 295 – 299: Did the recipient experience acute renal failure requiring dialysis?
Symptoms of renal failure include dehydration, nausea, blood in the urine, and / or swelling of extremities. Acute kidney failure is classified as three different stages:
- Stage 1
- Serum creatinine is 1.5 – 1.9 x baseline, or
- ≥ 0.3 mg/dL (≥ 26.5 µmol/L) increase
- Stage 2:
- Serum creatinine is 2.0 – 2.9 x baseline
- Stage 3
- Serum creatinine is 3.0 x baseline or
- Increase serum creatinine to ≥ 4.0 mg/dL (≥ 353.6 µmol/L) or
- The start of renal replacement therapy or
- In recipients < 18 years, decrease in eGFR to < 35 ml/min per 1.73 m2
If the recipient developed stage 2 or 3 acute renal failure, requiring dialysis (for less than three months) in the reporting period, report Yes and indicate the dialysis start and stop dates.
If dialysis was started in a prior reporting period and continued into the current reporting period, report the start date as Previously reported. If dialysis was stopped in prior reporting period but restarted in the current reporting period, report the start date as the date when dialysis was restarted.
Questions 300 – 304: Did the recipient experience chronic renal failure requiring dialysis?
Specify if the recipient experienced chronic renal failure (persistent decrease in glomerular filtration to < 60 mL/min.1.73m2 for three or more months), requiring dialysis in the reporting period. If Yes, indicate the dialysis start and stop dates.
If dialysis was started in a prior reporting period and continued into the current reporting period, report the start date as Previously reported. If dialysis was stopped in prior reporting period but restarted in the current reporting period, report the start date when dialysis was restarted.
Questions 305 – 306: Did the renal impairment / disorder resolve?
Indicate if the renal impairment / disorder resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. The resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed.
Table 5. Cardiac Impairments
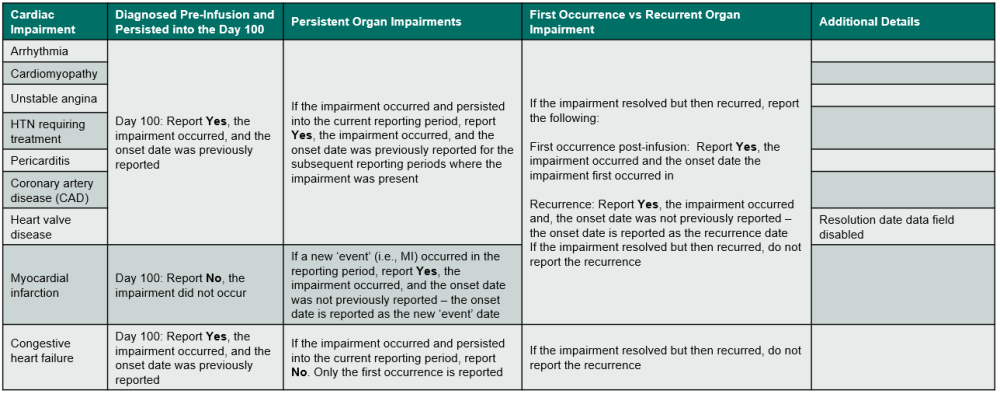
Questions 307 – 316: Did the recipient experience a cardiac impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced a cardiac impairment or disorder. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as cardiac impairment / disorder. Refer to Table 5. Cardiac Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions.
If the cardiac impairment or disorder is an arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, unstable angina, hypertension requiring treatment, pericarditis, coronary artery disease (CAD), or heart valve disease, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the cardiac impairment or disorder is congestive heart failure, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion or in a previous reporting period and the impairment recurred post-infusion.
If the cardiac impairment or disorder is myocardial infarction, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes if a myocardial infarction event occurred in the current reporting period, regardless of if this is the first or a subsequent event.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date as the date of the myocardial infarction event.
- Report No if a myocardial infarction did not occur in the current reporting period.
- Do not report myocardial infarction if it occurred prior to infusion and a new myocardial infarction did not occur in the current reporting period.
Cardiac Impairments and Disorders
- Arrhythmia: includes atrial fibrillation or flutter, sick sinus syndrome, and ventricular arrhythmia. If selected, specify the type of arrhythmia.
- Cardiomyopathy: a disease of the heart muscle that makes it more difficult for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body.
- Congestive heart failure (CHF): inability of the heart to supply oxygenated blood to meet the body’s needs. Ejection fraction < 40%. If selected, report the ejection fraction from diagnosis and specify if the recipient was Symptomatic or Asymptomatic.
- Coronary artery disease: damage or disease in the major blood vessels of the heart. Also called CAD, atherosclerotic heart disease.
- Unstable angina: sometimes called acute coronary syndrome and results in unexpected chest pain due to reduced blood flow and oxygen to the heart.
- Myocardial infarction (MI): an obstruction in the coronary artery resulting in damage / necrosis to the cardiac muscle.
- Hypertension (HTN) requiring therapy: report whether the recipient was still receiving therapy for hypertension on the contact date for the reporting period.
- Pericarditis: swelling and irritation of the pericardium.
- Heart valve disease: the presence of one or more of the following:
- Moderate or severe degree of valve stenosis or insufficiency as determined by echo, whether the valve is mitral, aortic, tricuspid or pulmonary
- Prosthetic mitral or aortic valve
- Symptomatic mitral valve prolapse
If the diagnosis was determined at an outside center and no documentation of a clinical, pathological, or laboratory assessment is available, the dictated date of diagnosis within a physician note may be reported.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
Questions 317 – 318: Did the cardiac impairment / disorder resolve?
Indicate if the cardiac impairment / disorder resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. For all cardiac impairments / disorders, except for cardiomyopathy, the resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed.
For cardiomyopathy, report the resolution date as the first date when the echocardiogram normalized, and the recipient is no longer receiving cardiomyopathy treatment. If an echocardiogram was not performed to assess the cardiomyopathy status, report the resolution date as the first date when treatment is no longer required and in the physician’s opinion, cardiomyopathy resolved.
This data field is disabled for heart valve disease.
Table 6. Vascular Impairments
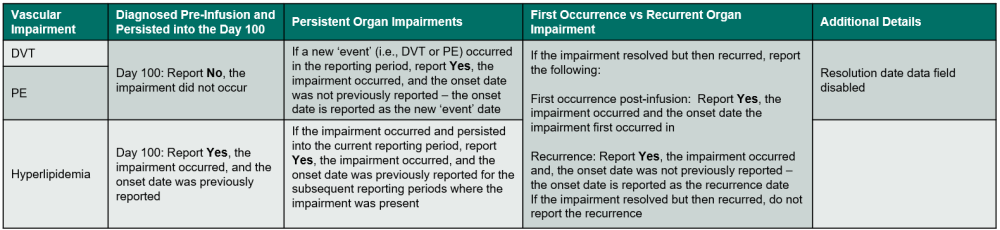
Questions 319 – 332: Did the recipient experience a vascular impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced a vascular impairment or disorder. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as vascular impairment / disorder. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions.
If the vascular impairment or disorder is a DVT or PE, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes if a DVT or PE event occurred in the current reporting period, regardless of if this is the first or a subsequent event.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date as the date of the DVT or PE event.
- Report No if a DVT or PE event did not occur in the current reporting period.
- Do not report DVT or PE if it occurred prior to infusion and a new DVT or PE did not occur in the current reporting period.
If the vascular impairment or disorder is hyperlipidemia, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
Vascular Impairments / Disorders
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): development of a blood clot in a deep vein. Specify if the DVT was catheter (central line) related. This information is typically documented within the results of the ultrasound.
- Pulmonary embolism (PE): development of a blood clot in the arteries of the lung. Specify if the PE was catheter (central line) related. This information is typically documented within the results of the ultrasound.
- Hyperlipidemia (high total cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol, high LDL cholesterol, and/or high triglyceride levels): high levels of lipids (fat particles) in the blood. Hyperlipidemia is typically diagnosed by a lipid panel. If this is reported, report the diagnosis date as the date when the lipid panel was drawn. Additionally, specify which lipids were assessed and provide the results (fasting results are preferred). Check all apply.
- If this is the first diagnosis or recurrence of hyperlipidemia, report the lab values from diagnosis / recurrence.
- If hyperlipidemia ‘persisted’ into the current reporting period, report the most recent lab values in the current reporting period.
Questions 333 – 334: Did the vascular impairment / disorder resolve?
Indicate if the vascular impairment / disorder resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. The resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed.
This data field is disabled if the impairment / disorder is DVT or PE.
Table 7. Neurological Impairments
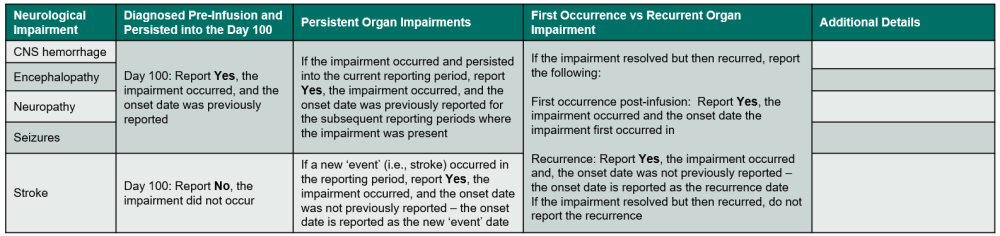
Questions 335 – 338: Did the recipient experience a neurological impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced a neurological impairment or disorder. Refer to Table 7. Neurological Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions.
If the neurological impairment or disorder is CNS hemorrhage, encephalopathy, neuropathy, or seizures, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the neurological impairment or disorder was a stroke, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes if a stroke occurred in the current reporting period, regardless of if this is the first or a subsequent stroke.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date as the date of the stroke.
- Report No if a stroke did not occur in the current reporting period.
- Do not report stroke if it occurred prior to infusion and a new stroke did not occur in the current reporting period.
- Do not report impacts / complications of a stroke that persist, only a stroke ‘event’ should be reported.
Neurological Impairments
- CNS hemorrhage: bleeding within the central nervous system.
- Encephalopathy: damage or disease of the brain. Symptoms of encephalopathy include memory loss, personality changes, and declining ability to concentrate and reason.
- Neuropathy: nerve damage, usually in hands and feet, which causes pain, weakness, and numbness.
- Seizures: sudden, involuntary muscle contractions due to the hyperexcitation of neurons.
- Stroke / transient ischemic attack: loss of brain function due to a disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. If the recipient experienced different kinds of strokes in the reporting period, report a separate instance for each type of stroke.
Questions 339 – 340: Did the neurological impairment / disorder resolve?
Indicate if the neurological impairment / disorder resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. The resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed.
Table 8. Endocrine Impairments
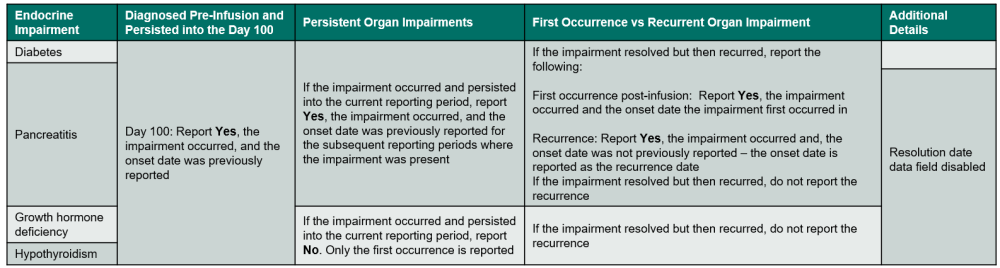
Questions 341 – 349: Did the recipient experience a endocrine impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced an endocrine impairment or disorder. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as an endocrine impairment / disorder. Additionally, refer to Table 8. Endocrine Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions.
If the endocrine impairment / disorder is diabetes or pancreatitis, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the endocrine impairment / disorder is growth hormone deficiency or hypothyroidism, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion or in a previous reporting period and the impairment recurred post-infusion.
Endocrine Impairments
- Diabetes / hyperglycemia requiring chronic treatment: high blood glucose levels. Diabetes / hyperglycemia should only be reported if insulin and / or oral medication is required for treatment. Diabetes / hyperglycemia controlled through diet and exercise should not be reported. Only select this option if the recipient developed diabetes / hyperglycemia requiring treatment post-infusion.
- Growth hormone deficiency / short stature: a condition in which the body does not produce enough growth hormone / a reduced overall rate of growth.
- Hypothyroidism requiring replacement therapy: decreased activity of the thyroid gland. Diagnosis of hypothyroidism includes high levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, depression, weakness, weight gain, musculoskeletal pain, decreased taste, hoarseness, and / or puffy face.
- Pancreatitis: inflammation of the pancreas.
Questions 350 – 351: Did the endocrine impairment / disorder resolve?
Indicate if the endocrine impairment / disorder resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. The resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed
This data field is disabled for growth hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism, and pancreatitis.
Table 9. Genitourinary Impairments
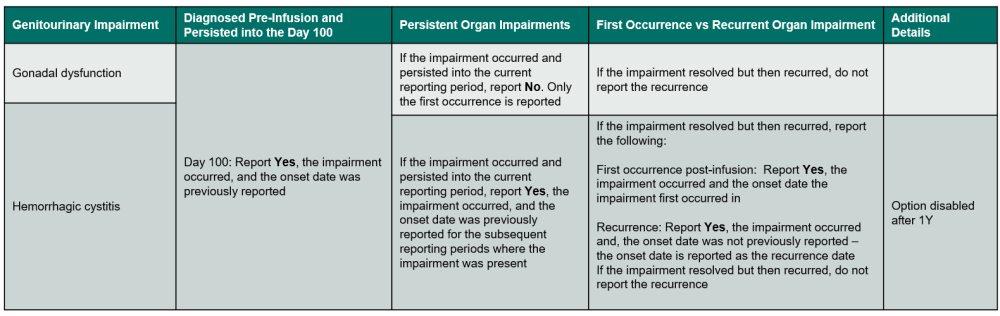
Questions 352 – 355: Did the recipient experience a genitourinary impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced a genitourinary impairment or disorder. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as neurological impairment / disorder. Refer to Table 9, Genitourinary Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions.
If the genitourinary impairment / disorder is gonadal dysfunction, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion or in a previous reporting period and the impairment recurred post-infusion.
If the genitourinary impairment / disorder is hemorrhagic cystitis, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
Genitourinary Impairments / Disorders
- Gonadal dysfunction requiring hormone replacement (testosterone or estrogen): Females may experience early symptoms of menopause including amenorrhea. Males may experience decreased spermatogenesis. Low levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and / or testosterone may require hormone replacement therapy.
- Hemorrhagic cystitis / hematuria requiring medical intervention (catheterization of bladder, extra transfusions, urology consult): characterized by bleeding and inflammation of the bladder wall. Hemorrhagic cystitis may result from systemic chemotherapy or radiation therapy and / or some viral infections (e.g., BK virus). Report cases with macroscopic (visible to the naked eye) or gross hematuria (WHO Grade III and IV hemorrhagic cystitis). If the etiology is infectious, also report in the Infection section. Examples of medical intervention include catheterization of bladder, extra transfusions, or a urology consultation.
Questions 356 – 357: Did the hemorrhagic cystitis / hematuria requiring medical intervention resolve?
Indicate if the hemorrhagic cystitis / hematuria requiring medical intervention resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. The resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed.
Table 10. Musculoskeletal Impairments
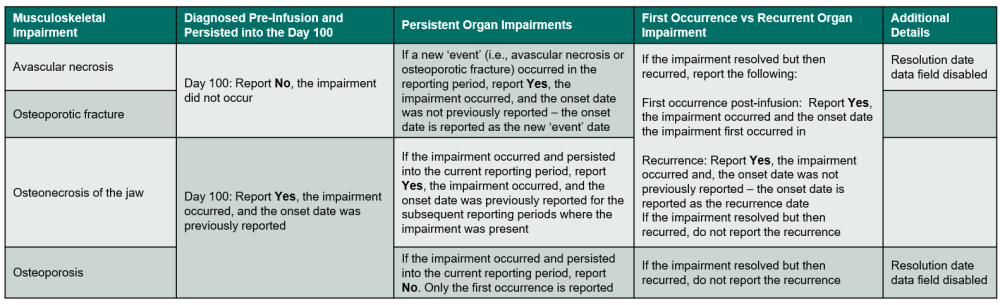
Questions 358 – 363: Did the recipient experience a musculoskeletal impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced a musculoskeletal impairment or disorder. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as neurological impairment / disorder. Refer to Table 10. Musculoskeletal Impairment for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions.
If the musculoskeletal impairment / disorder is avascular necrosis or osteoporotic fracture, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes if an avascular necrosis event or osteoporotic fracture occurred in the current reporting period, regardless of if this is the first or a subsequent event / fracture.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date as the date of the avascular necrosis event or osteoporotic fracture.
- Report No if an avascular necrosis event or osteoporotic fracture did not occur in the current reporting period.
- Do not report an avascular necrosis event or osteoporotic fracture if it occurred prior to infusion and a new avascular necrosis event or osteoporotic fracture did not occur in the current reporting period.
If the musculoskeletal impairment / disorder is osteonecrosis of the jaw, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
If the musculoskeletal impairment / disorder is osteoporosis, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period or prior to infusion and persisted into the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion or in a previous reporting period and the impairment recurred post-infusion.
Musculoskeletal Impairments
- Avascular necrosis: localized tissue death due to inadequate oxygen to the cells. Also known as coagulation necrosis or ischemic necrosis.
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw: bones of the jaw weaken and die due to potent antiresorptive medications such as bisphosphonates or RANKL inhibitors, infection, steroid use, and treatment of cancer, including radiation.
- Osteoporosis: bones become weak and brittle due to losing bone mass faster than it is created from aging.
- Osteoporotic fracture: fractures due to low bone mineral density.
Table 11. Psychiatric Impairments
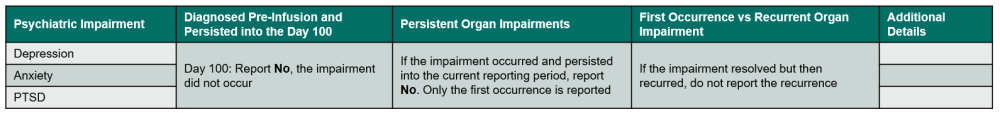
Questions 364 – 367: Did the recipient experience a psychiatric impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced a psychiatric impairment or disorder, requiring medication. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as neurological impairment / disorder. Refer to Table 11. Psychiatric Impairment for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions.
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period or prior to infusion.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion or in a previous reporting period and the impairment recurred post-infusion.
Psychiatric Impairments / Disorders
- Depression requiring therapy: mood disorder resulting in persistent feeling of sadness and loss of interest. Common treatments include antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antipsychotic medications. Common names include Amitriptyline, Bupropion (Wellbutrin), Buspirone, and Abilify.
- Anxiety requiring therapy: disorder characterized by feelings of worry, anxiety, or fear which are strong enough to interfere with daily activities. Common medications include Duloxetine (Cymbalta), Diazepam (Valium), Buspirone, Pregabalin (Lyrica).
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) requiring therapy: condition triggered by seeing or experiencing a traumatic event.
Table 12. Other Impairments
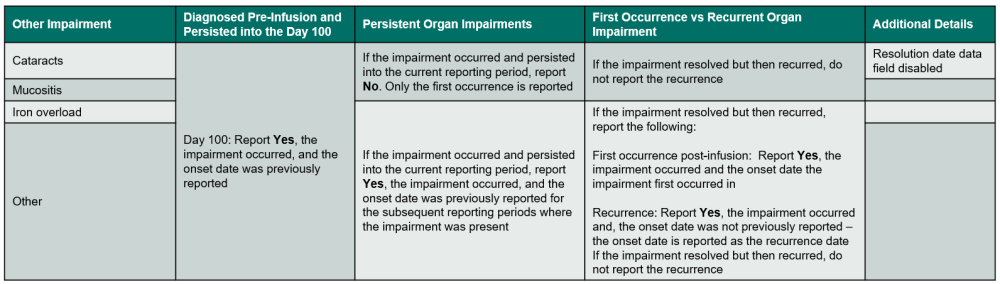
Questions 368 – 377: Did the recipient experience a other impairment / disorder?
Indicate if the recipient experienced an other impairment or disorder. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as other impairment / disorder. Refer to Table 12. Other Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions
If the other impairment / disorder is cataracts or mucositis, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted into the Day 100 reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period or prior to infusion and persisted into the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion or in a previous reporting period and the impairment recurred post-infusion.
If the other impairment / disorder is iron overload or other, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No:
- Report Yes in the following scenarios:
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date.
- The impairment was diagnosed in a previous reporting period and persisted into the current reporting period.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a prior reporting period but recurred in the current reporting period.
- Report No, the onset date was not previously reported and specify the diagnosis date of the recurrence.
- The impairment was diagnosed prior to infusion and persisted post-infusion.
- Report Yes, the onset date was previously reported.
- The impairment is diagnosed for the first time in the current reporting period.
- Report No in the following scenarios:
- The impairment was not diagnosed in the current reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved in a previous reporting period.
- The impairment was diagnosed and resolved prior to infusion.
Other Impairments
- Cataracts: loss of transparency in the lens of the eye.
- Iron overload requiring therapy: condition characterized by having too much iron in the body. Therapy includes phlebotomy and iron chelation. Indicate which therapy is required. Check all apply.
Iron overload cannot be answered on the day 100 form. Iron overload questions will be answered for all subsequent reporting periods.
- Mucositis requiring therapy: inflammation and ulceration of mucous membranes that line the digestive tract, usually due to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Specify the grade as 0 (none), I (mild) – oral soreness, erythema, II (moderate) – oral erythema, ulcers, solid diet tolerated, III (severe) – oral ulcers, liquid diet only, or IV (life-threatening – oral ulcers, oral alimentation impossible in question 304. The highest grade in the reporting period should be reported. Do not report mucositis which did not require treatment or intervention during the reporting period.
Mucositis can only be answered on the day 100 form. Mucositis questions will be skipped for all subsequent reporting periods.
- Other impairment or disorder: use this category to report any clinically significant impairment(s) / disorder(s) not listed on the form. Specify the other impairment / disorder.
Do not report complications that have been reported elsewhere on the form.
Questions 378 – 382: Has the recipient received a solid organ transplant since the date of last report?
Indicate whether the recipient received a solid organ transplant since the date of the last report. If Yes, specify the organ transplanted. If Other organ is reported, specify organ. Additionally, report the date of the solid organ transplant and specify the solid organ donor type.
For more information regarding reporting partial or unknown dates, see General Instructions, General Guidelines for Completing Forms.
If the recipient did not receive a solid organ transplant during the reporting period, report No.
Solid organ transplant questions cannot be answered on the day 100 forms. These questions will be answered for all subsequent reporting periods.
Section Updates:
| Question Number | Date of Change | Add/Remove/Modify | Description | Reasoning (If applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q250 – 377 | 7/26/2024 | Modify | Instruction overhaul for reporting organ impairments | Due to further discussions with leadership |
| Q275 | 3/13/2024 | Add | Instructions added on when to use the medication toxicity for liver impairment: Medication toxicity: If the liver abnormality (i.e., abnormal LFT values) is associated with drug initiation, abnormalities improve with cessation, and / or there are no other causes for the change. | Missing instructions |
| Q307 | 4/19/2025 | Add | Instructions clarified when to report Yes or No for coronary artery disease: _Indicate if the recipient experienced a cardiac impairment or disorder. Review the list below to determine if the condition should be reported as cardiac impairment / disorder. Refer to Table 5. Cardiac Impairments for an overview of when to report the impairment. If Yes, report the onset date, specify if the impairment / disorder, and answer any other applicable questions. If the cardiac impairment or disorder is an arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, unstable angina, hypertension requiring treatment, pericarditis, coronary artery disease (CAD), or heart valve disease, use the following guidelines to determine when to report Yes or No: | Missed cardiac organ impairment from original instructions |
| Q317 | 11/17/2023 | Add | Instructions added on how to report the resolution date for cardiomyopathy: _Indicate if the cardiac impairment / disorder resolved during the reporting period. If Yes, report the resolution date. For all cardiac impairment / disorders, except for cardiomyopathy, the resolution date is the date when the notes specify the condition as resolved and / or medications to treat the condition were completed. For cardiomyopathy, report the resolution date as the first date when the echocardiogram normalized, and the recipient is no longer receiving cardiomyopathy treatment. If an echocardiogram was not performed to assess the cardiomyopathy status, report the resolution date as the first date when treatment is no longer required and in the physician’s opinion, cardiomyopathy resolved. | Due to changes in FormsNet3 validations |
| Q341 | 1/24/2025 | Remove | Update diabetes / hyperglycemia requiring chronic treatment description to match Table 8: Endocrine Impairments
|
Updated to match organ impairment table |
Need more help with this?
Don’t hesitate to contact us here.

