The U.S Court Systems
If the State thinks you have committed a crime, the District Attorney’s Office, representing the State, may bring criminal charges against you. Only the State – not another person or agency – can charge you with a criminal violation.
There are three different kinds of criminal cases: infractions, misdemeanors, and felonies.
- An infraction is a minor violation. Some traffic violations are infractions.
- A misdemeanor is a more serious crime that can be punished by up to 1 year in jail. Click here to learn more about misdemeanors
- A felony is the most serious kind of crime. If you are found guilty, you can be sent to state prison or receive the death penalty.
The Federal courts are similar in structure to State courts in California. The Supreme Court is the highest in our country’s judiciary.
There are two levels of federal courts under the Supreme Court.
- The U.S. District Courts (the Trial Courts), and
- The U.S. Courts of Appeals (the Appellate Courts).
U.S. District Courts
The U.S. District Courts are the Trial Courts of the Federal court system. The District Courts can hear most Federal cases, including civil and criminal cases. There are 94 U.S. District Courts in the U.S. and U.S. territories. Each district includes a United States bankruptcy court. Some states, like Alaska, have only 1 District Court for the whole state. Others, like California, have several.
Two special Trial Courts hear certain kinds of cases anywhere in the country:
- The Court of International Trade hears cases about international trade and customs issues.
- The U.S. Court of Federal Claims hears cases about claims for money damages against the United States, disputes over federal contracts, unlawful “takings” of private property by the federal government, and other claims against the United States.
- THE U.S. Courts of Appeals*
The U.S. District Courts are organized into 12 regional circuits, and each has a U.S. Court of Appeals. There is also one Court of Appeals of the Federal Circuit. This court has nationwide jurisdiction to hear appeals in specialized cases, like patent law cases and cases decided by the Court of International Trade and Federal Claims. A Court of Appeals hears appeals from the district courts in its circuit. It can also hear appeals from decisions of federal administrative agencies.
U.S. Supreme Court
The United States Supreme Court has a Chief Justice and eight associate justices. The Supreme Court can choose a limited number of cases from the cases it is asked to decide. Those cases may begin in the Federal or State courts. And, they usually involve important questions about the Constitution or federal law.
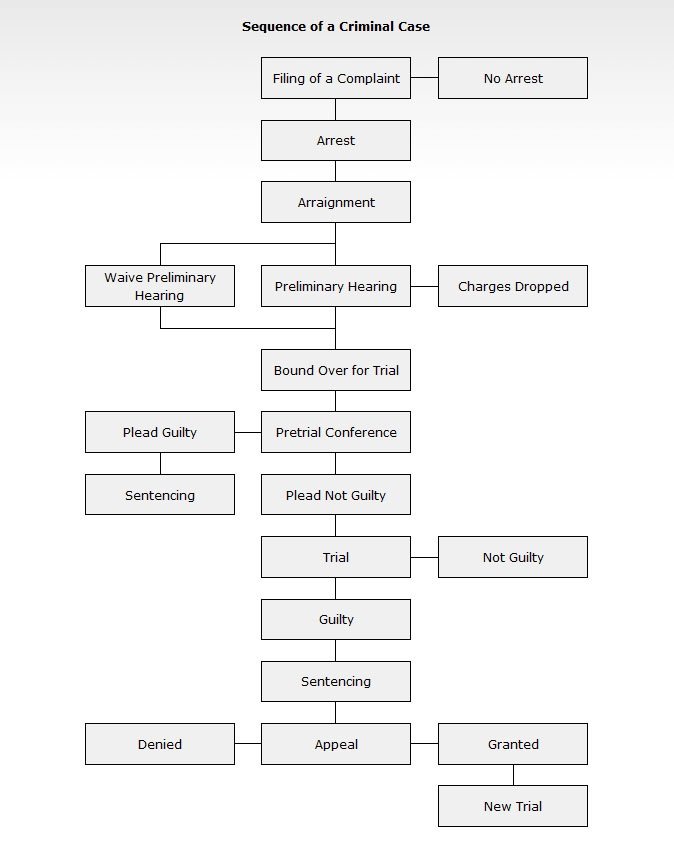
Here is a flowchart that shows how criminal cases move through the court system.



Post your comment on this topic.