ANALYTICAL TESTING REPORT REQUIREMENTS
Laboratories that conduct the above tests must be accredited under ISO 17025 for the test methods they use.
APPROVED ALTERNATIVES TO CDPH STANDARD METHOD FOR VOC EMISSIONS
The information below contains additional international testing standards and reference methods that ILFI has approved as comparable achievement to the CDPH v1.1-2010 / v1.2-2017 requirements and associated VOC emissions limits. All interior products with the potential to emit, including wet-applied products, that do not meet CDPH compliance must be third-party tested at an ISO 17025-certified laboratory by one of the following acceptable standards, and meet the VOC thresholds listed below.
These standards and protocols may include different testing methods, parameters, and chamber sizes, among other parameters, but are considered comparable to CDPH methods and VOC emissions limits for the requirements of this Imperative and for the purposes of the Living Building Challenge. However, interior products using these standards and thresholds must additionally comply with a maximum emission concentration of 10ug/m3 for formaldehyde, as is required for CDPH compliance.
Table 10-3 Alternate Compliance for Interior Products
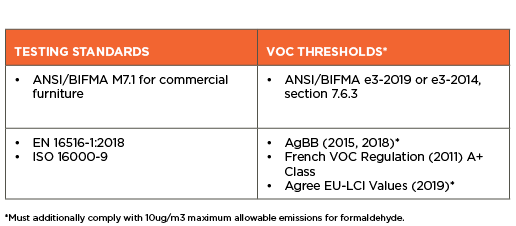
Table 10-4 Alternate Compliance for Furniture
CDPH COMPONENTS
When all applicable components of a constructed product are CDPH compliant and have been individually tested, the final product does not require individual testing. Teams must provide CDPH documentation for each of the relevant components.
CDPH CONFORMANT CERTIFICATIONS
Projects may use products tested and certified under the certifications included in the list of certifications and programs that use CDPH Standard Method v1.2 maintained by the California Department of Health on its website. Project teams may also submit a Request for Ruling for preapproval to make the case for conformance of additional certifications. The Request for Ruling submission must contain supporting documentation that clearly demonstrates conformance to CDPH v1.1 or v1.2 VOC thresholds.
CDPH STANDARD METHOD V1.1-2010
The California Department of Public Health’s Standard Method v1.1-2010 (CDPH) is an emissions testing and evaluation standard intended to be applied to any product with the potential to emit VOCs generally used within the envelope of an enclosed indoor environment that can be tested whole or by representative sample in environmental chambers. This method specifies target chemicals and their maximum allowable concentrations. In 2017, CDPH v1.2-2017 was issued, and is an accepted alternate to CDPH v1.1-2010 for the purposes of this Imperative.
CERTIFICATIONS CONFORMANT TO OTHER APPROVED EMISSIONS STANDARDS
Projects using products tested under an approved alternative to CDPH SM v1.1-2010 / v.1.2-2017 may use one of the certifications listed below or submit for preapproval, a Request for Ruling to make the case for conformance of another certification. The Request for Ruling submission must contain supporting documentation that clearly states conformance to the VOC thresholds contained in the approved CDPH alternatives, currently AgBB, French VOC Regulation A+ class, or Agreed EU-LCI values. In addition, laboratories that conduct any emissions testing for the proposed certification must be accredited under ISO 17025 for the test methods they use.
Certifications Conformant to Approved CDPH Alternatives:
- Blue Angel (Der Blauer Engel) DE-UZ 113
- For floor coverings, flooring underlays, thermal insulation, indoor wall paints, and varnishes, glazes and primers.
- May be used for furniture only if maximum allowable concentrations allowed by ANSI/BIFMA e3-2014e Furniture Sustainability Standard, Section 7.6.3 are met.
- EMICODE EC1 and EMICODE EC1PLUS
- Finnish Emission Classification of Building Materials: M1
- Indoor Air Comfort GOLD
EMISSIONS REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
The LBC requires individual concentration results for each of the target VOCs as outlined in any of the Approved Product Emissions Standards for building products with the potential to emit that are installed in the project. These individual concentration results do not need to be additionally submitted if a product has already qualified for the Approved Product Emissions Standard, though the standard or certification documentation that is submitted must clearly indicate that all applicable target VOC thresholds were met. The laboratory certificate of compliance or associated summary report must either have an expiration date after, or a testing date within the three years prior to, the date of specification (at the time of material research and vetting for the project).
Total VOCs (TVOCs) or any form of combined VOC results that are not accompanied by individual concentration results are not accepted as IAQ Testing in this Imperative unless explicitly stated through an existing LBC Temporary Exception.
EVALUATION OF PRODUCTS WITH POTENTIAL VOC EMISSIONS
Interior building products with the potential to emit VOCs and that are intended for installation within the building envelope (defined as interior of the wall vapor barrier and roof vapor barrier) must demonstrate emissions testing to the CDPH Standard Method v1.1-2010, or other ILFI-approved product emissions Testing Standards (see Table 10-3) and comply with individual VOC Thresholds established in the Testing Standard.
Interior site-installed, wet-applied products (e.g., paints, coatings, adhesives and sealants) are also held to the CDPH emissions testing requirements of this Imperative, in addition to meeting VOC content limits as required by Imperative 13, Red List.
INHERENTLY NON-EMITTING SOURCES
Products that are considered inherently non-emitting sources of VOCs and have no integral organic-based surface coatings, binders, or sealants, are not required to demonstrate compliance to CDPH limits on VOC emissions. These products include stone, ceramic, powder-coated metals, plated or anodized metal, glass, concrete, clay brick, certified organic fabrics and upholstery, and unfinished or untreated solid wood.
Salvaged and reused products that are 12 months old, and in-situ materials, are also considered inherently non-emitting for the purposes of this Imperative and are not required to comply with CDPH.
MARKET LIMITATIONS
To address instances when a CDPH compliant product is not available in the market. Project teams may research and advocate for compliant products and install a small number of untested or noncompliant products using Exception HH-003. Note that installing products that are not CDPH compliant may impact a project’s ability to meet IAQ testing thresholds.
PRODUCTS CONTAINING COMPOSITE OR ENGINEERED WOOD
Project teams should request additional VOC emissions documentation to an aforementioned standard or certification for composite wood products, or products that contain composite wood, to meet the requirements of this Imperative. Documentation and certifications that demonstrate low formaldehyde emissions, such as CARB ASTM and/or TSCA Title VI Compliance or BIFMA X7.1 testing, must be supplemented by additional documentation demonstrating CDPH / Approved Products Emission Standards Compliance for the purposes of the Living Building Challenge.
PRODUCTS BY COST
For project teams calculating their CDPH-compliant product thresholds by cost, refer to Materials Construction Budget Clarifications for guidance on cost basis.
STRUCTURAL MEMBERS – COMPOSITE OR ENGINEERED WOOD
The CDPH Standard excludes structural material. Project teams are advised that while structural material is not subject to the requirements of CDPH, depending on where they’re used, composite structural members could influence the results of the indoor air quality test, which references formaldehyde and a number of other VOCs. In addition, for projects pursuing I13 Red List, ingredients requirements remain applicable, including those related to formaldehyde.
With respect to composite or engineered structural wood, prioritizing products that meet applicable standards identified in APA Technical Note J330D will best position projects for compliance with formaldehyde-related requirements within LBC. The Technical Note lists USA and Canadian production specifications for structural wood and compares the formaldehyde emissions to other international specifications and formaldehyde emissions thresholds for these products.