WHAT IS A MODEL
3D modelling is the process of developing a mathematical representation of any three dimensional object.
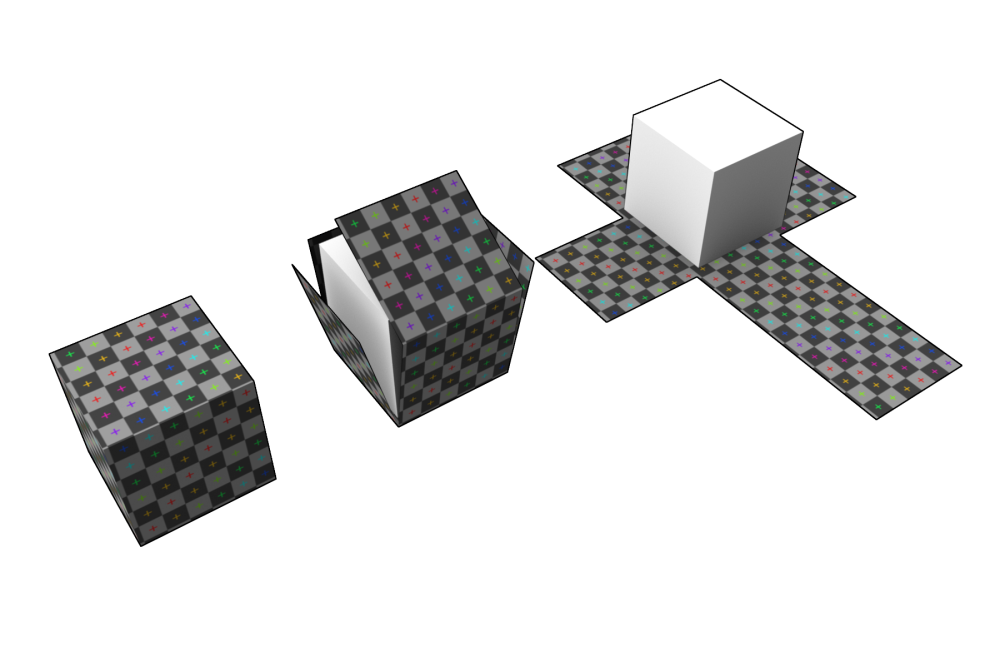
A model is made of points in 3D space also known as vertexes. These vertexes are joined by lines. Once 3 points have been joined by lines it creates a triangle these triangles are also known as faces or polygons. Many of these faces joined together create what we call a 3D Model.
NORMALS
To view your models Normals see Mesh Edit
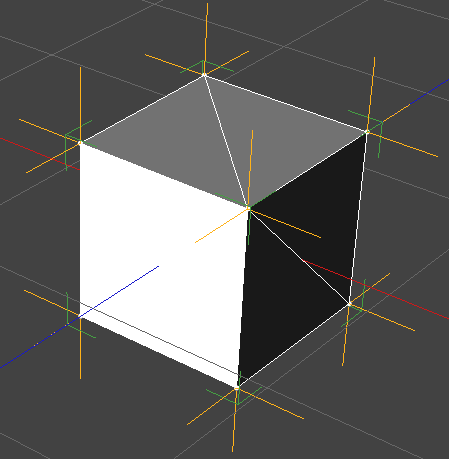
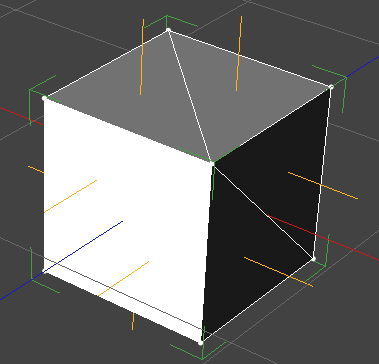
Faces and vertexes can contain normal data. A normal is the direction of the face or vertex and they are generated in 3D modelling software. Normals are commonly used for lighting algorithms. You would commonly expect normals to be facing outwards.
If you encounter normal issues or are curious about your objects normals you can view them in SHAPE.
To view a models normals,
Right click on the model, Mesh Edit,
Right click on the model, Options, Normals,
You have the option to view the Vertex, Face or None.
UV MAP
To Edit your models UV map see Editing UVs
A 3D model can contain UV map data. UV mapping is the process of converting 3D vertex coordinates into 2D coordinates. This process is how the computer knows how to wrap a 2D video around a 3D object. Similar to cutting the net of a box out of a 2D piece of paper and folding it into a 3D box.
If the model file does not contain UV map data video will appear on the model in a random way. When importing a model without UV map data into SHAPE, SHAPE will give you a message to tell the user UV map data is not present. However, video can still be applied to the object using Planar or Perspective texturing.