The different planes
Measurements taken and files produced with Flexijet and the FlexiCAD software are most commonly done using planes. A plane can be pictured as a virtual infinite surface upon which measurements are set. All measurements that are made with Flexijet are translated perpendicular to the current plane.
Working with planes has the following advantages:
- The measurements are more precise because we can choose measurement points for optimum clarity that will be projected to the plane rather than needing to get exact corners of objects
- The editing of measured objects, such as trimming, stretching, rounding and so on, is possible when the objects (lines, arcs) are on one plane.
Horizontal plane
![]()
A horizontal plane defines an infinite surface that is parallel to the horizon.
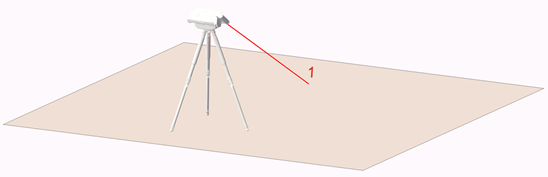
Picture a large horizontal surface. You could move it upwards to the sky and down to the floor. Only one measurement point is required to set a level horizontal plane. This one point determines the height of the horizontal plane. Horizontal planes are used when it can be assumed that the surface is almost horizontal. The floor plan of a room, a countertop surface, and a flat ceiling are generally measured with a horizontal plane.
Setting a Horizontal Plane
Create a new folder from the measurement ribbon and select ‘Horizontal plane,” or in the Project Explorer, click to select the folder for which you want to define a plane. In the Measurement tab, in the group Planes, click on Horizontal Plane.
If measuring a floor, this plane would typically be set with a single point on the floor.
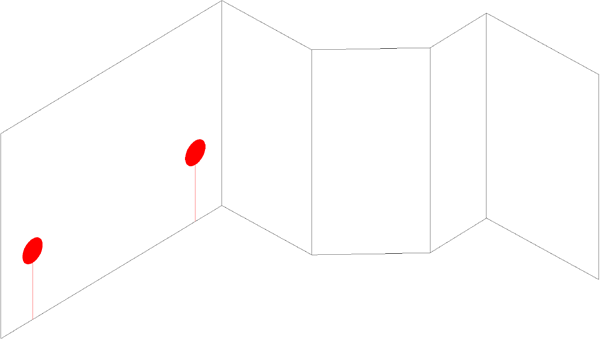
Note: Horizontal planes are always viewed from the top, or plan view! It’s a good practice to leave a note on a horizontal plane such as a shower ceiling to remember to mirror or flip this plane prior to fabricating!
Vertical plane
![]()
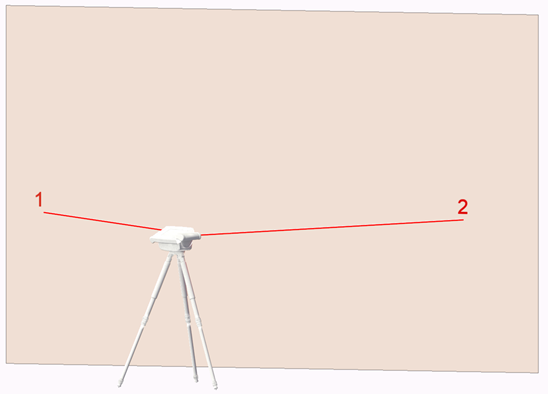
A vertical plane is a plane that is perpendicular to the horizon, such as a vertical wall. It is basically a precisely aligned wall that stretches from the ground straight to the sky.
It is always defined with 2 points. The two points should be as far apart horizontally (from left to right) as possible and cannot be measured above each other.
Setting a Vertical Plane
Create a new folder from the measurement ribbon and select ‘Vertical plane,” or in the Project Explorer, click to select the folder for which you want to define a plane. In the Measurement tab, in the group Planes, click on Vertical Plane.
In the command window, you will be prompted to measure the first point on the left and then the second point on the right.
Free plane
![]()
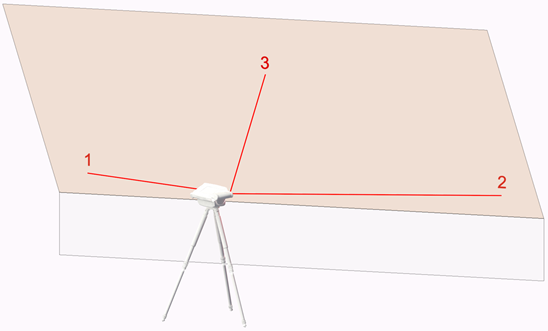
A free plane is a plane that can be oriented in any direction. A free plane can be a roof slope, for example, which you can picture as an infinite flat surface with the pitch of the roof.
A free plane is set with 3 points, which span a preferably large triangle.
Setting a Free Plane
Create a new folder from the measurement ribbon and select ‘Free plane,” or in Project Explorer, click to select the folder for which you want to define a plane. In the Measurement tab, in the group Planes, click on Free plane.
In the command window, you will be prompted to measure the first point on the bottom left, then the second point on the bottom right, and the third point on the top (center).
Redefine Plane
This function will redefine the plane of a folder. Note that this will not change the position of elements in a folder!
This function can be used to reverse the view of a vertical folder, for example.
How to redefine a plane
From the measurement ribbon, select the ‘Rededine plane’ function or just right-click on the folder where the plane will be redefined in the project explorer.

Set up the new folder. Note: This function does not change the position of the elements; a 2D projection needs to be done to project elements on the new position of the plane.
Remove plane
A plane may be removed from a folder with an assigned plane. Note that removing a plane does not change the geometry or location of the existing elements in a folder.
This function can be accessed by selecting the desired folder in the Project Explorer, right-clicking on it, and selecting Plane>Remove Plane

After this, the folder icon will no longer show the assigned layer and will display the blank folder icon instead of a plane icon.
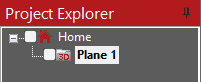
Show plane
FlexiCAD provides the option to see a visual representation of a plane as a rectangle in your measurement file. This function can be useful for visually verifying that a plane is set properly, especially in projects with multiple planes. This tool does not create a permanent object, and the visual representation of the plane is removed by using the ‘Escape’ key.
To use this function
- In Project Explorer, Right click on the 2D folder in which you wish to see the plane. Then select ‘Plane> Show Plane’.
- To visualize your plane, you may navigate to the parent 3D folder or Project folder containing the 2D folder and manipulate the 3D view using the Dynamic View tool.
- To remove the visual representation of the plane, press ‘Escape’ or cancel.
h4. Watch the video tutorial here:
2D-Projection – Flattening all elements on a plane.
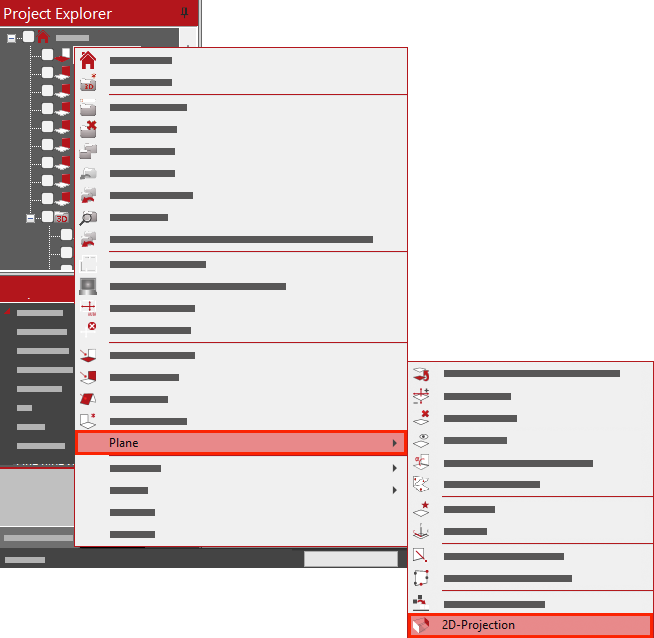
The function ‘2D-Projection’ will flatten all elements in the current folder to the current plane. This is useful if elements were traced from another folder in 3D-snap mode instead of 2D-snap mode. Learn more about 2D-Projection here.
More folder options
Folder functions of the Project Explorer are in the pop-up menu: Select one folder with the left mouse button and then click the right mouse button to bring up the menu.
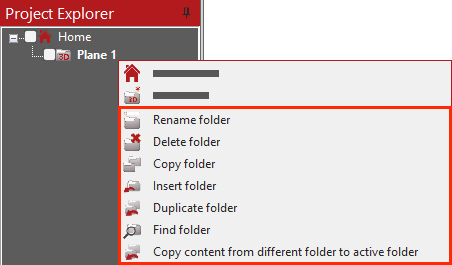
| Rename folder’ | Is used to rename the selected folder. Tip: Ensure your cursor remains over the Project Explorer |
| ‘Delete folder’ | Is used to delete the selected folder. |
| ‘Copy folder’ | Is used to copy a folder to the clipboard, in order to paste it later in another place of the Explorer. |
| ‘Paste folder’ | Is used to paste a folder that has previously been copied to the clipboard. |
| ‘Duplicate folder’ | Is used to make a duplicate copy of the selected folder including its elements in the same plane. |
| ‘Find folder’ | Is used to find a folder by measuring a point on that folder’s plane. If you start a measurement on the plane, the corresponding folder of the plane is selected automatically. |
| ‘Copy content from different folder to active folder’ | It is used to copy elements from one folder to another folder. Note that this will not modify the position of the elements. |
Elements can be copied between folders in a variety of ways.
Ctrl-c and Ctrl-v (Copy-paste method)
This method can be used to copy and paste elements from one folder to another. Most elements will be pasted on the plane of the destination folder; for example, vertical elements in a vertical folder can be copied and pasted horizontally on a horizontal folder.
- First, select all the desired elements that you wish to copy. In Touch mode, use the ‘Select objects’ tool. (see ‘Touch-Mode/PC-Mode’ for more information)
- Use ‘Ctrl-c’ to copy elements. The command line will read ‘XX elements copied to clipboard’
- Now, navigate to the destination folder. Use ‘Ctrl-v’ to paste and click/tap the insertion point on the page, or use the command line/coordinates window to specify an insertion point. The objects will be pasted on the active plane of the page.
Copy content from different folder to active folder
This It is used to copy elements from one folder to another folder. _Note that this will not modify the position of the elements.
Click here if you want to learn more about this function. ‘Copy content from different folder to active folder’





Post your comment on this topic.