The SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers) model is a powerful tool for process analysis and improvement. It provides a high-level view of the key elements in a process, enabling companies to better understand and optimize their workflows.
Why Use SIPOC?
- Clarity in Process Mapping: SIPOC helps organizations clarify what goes into a process (inputs) and what comes out (outputs), making it easier to define, analyze, and improve processes.
- Enhanced Communication: By laying out Suppliers, Inputs, Processes, Outputs, and Customers, SIPOC facilitates clearer communication across departments, ensuring everyone understands the process from start to finish.
- Streamlined Process Improvement: SIPOC tables serve as a foundational tool for identifying areas of improvement, ensuring that all relevant elements are considered in process enhancement projects.
What is SIPOC?
SIPOC is a diagram used in process mapping that outlines the Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, and Customers involved in a given process.
Here’s how SIPOC elements are defined:
| Supplier | The entity that provides input(s) to a process. |
| Inputs | All items used to produce one or more outputs from a process. |
| Process | The actual process being analyzed or improved. |
| Outputs | The products, services, or information that emerge from a process. |
| Customers | The entity that uses the outputs generated from the process. |
Where to View a Process’ SIPOC
the SIPOC data can be viewed in a process’ Details view if it has been defined. SIPOC can be established in two ways:
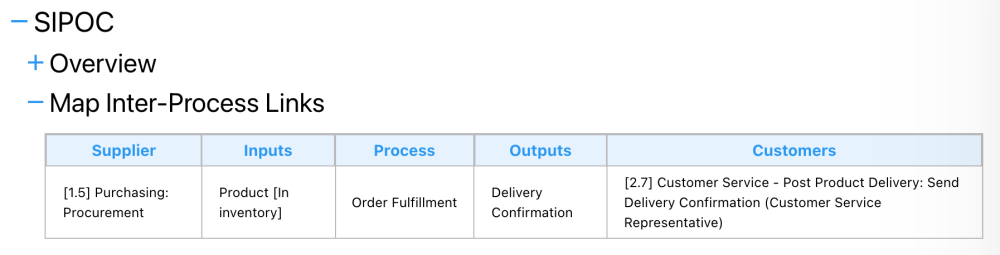
1. Using the Map’s Inter-Process Links
This method relies on inter-process links to connect related processes. With this method, SIPOC tables display data in the Details view only when at least one IPL is created. This approach can be effective for organizations that have established processes with clear links and inputs/outputs between them, providing a structured view of how different processes interact.
How to Define SIPOC Using this Method
- Navigate to the Diagram view of the process.
- Click the Edit button to access the Diagram Editor.
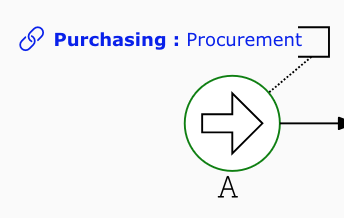
- Define an IPL for both the start event(s) and end event(s) of the process.
- These will be shown as Suppliers and Customers in the SIPOC table.
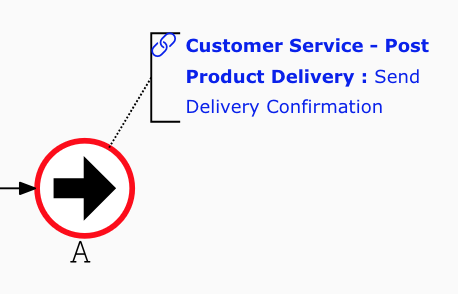
- Navigate to the start event’s linked process. In its Diagram Editor, define the Inputs/Outputs for its end event.
- These will become the Inputs in the original process’s SIPOC table.
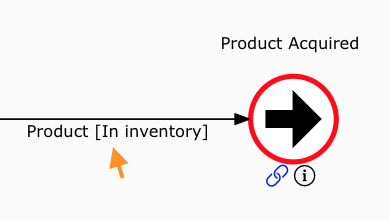
- Next, navigate to the end event’s linked process. In its Diagram Editor, define the Inputs/Outputs for its start event.
- These will become the Outputs in the original process’s SIPOC table.
- Return to the Details view of the original process.
- Open the ‘SIPOC’ accordion, and then expand the ‘Map Inter-Process Links’ sub-accordion.
- The SIPOC table will now be displayed.
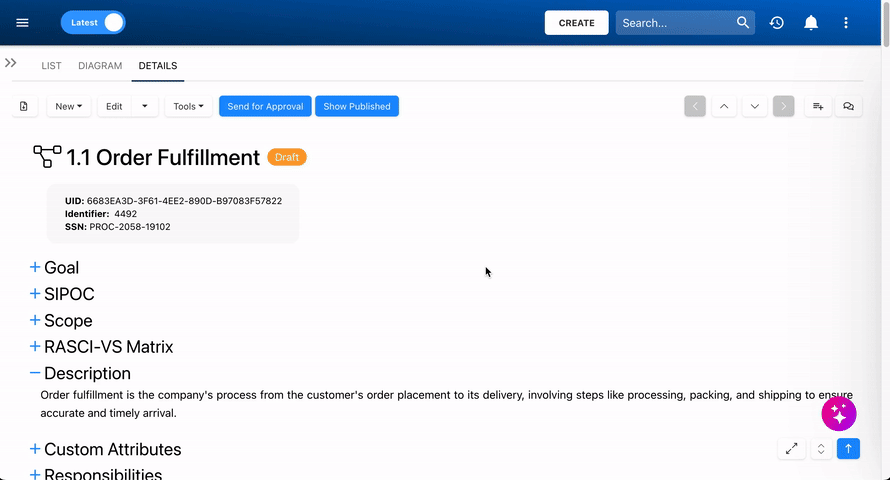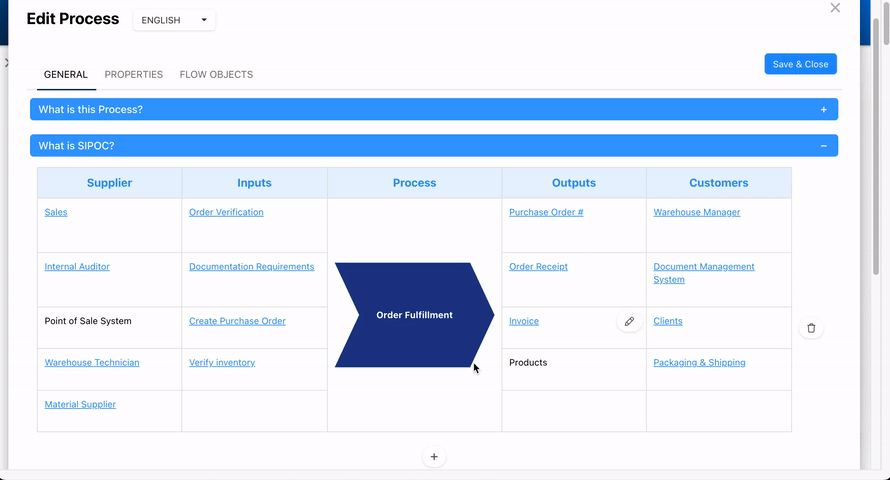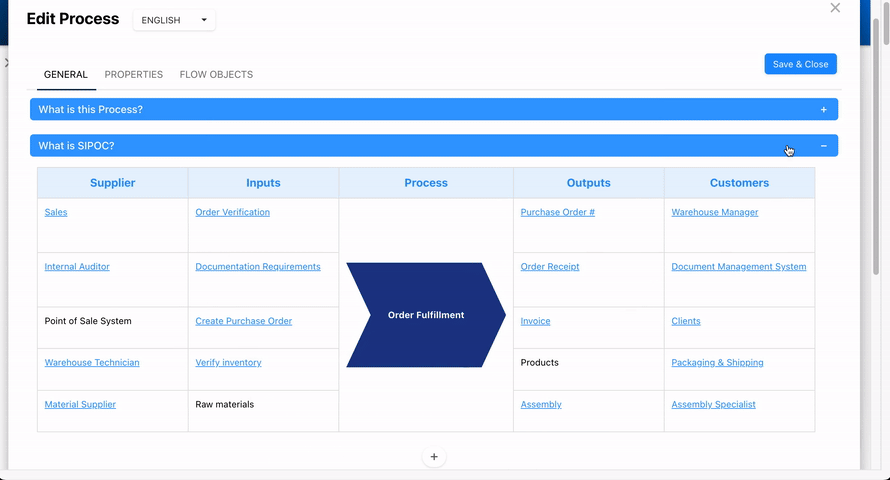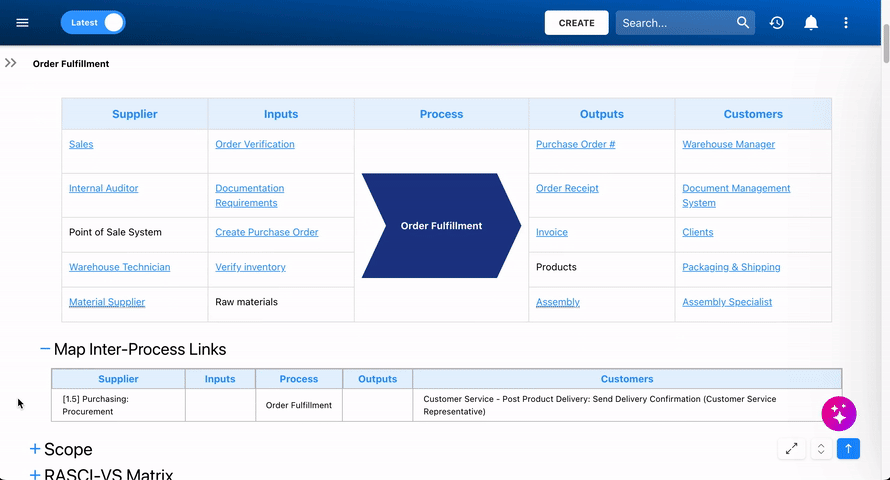
2. Building Your Own Customized SIPOC Table
This feature allows Modelers to directly define and manage SIPOC elements within the process creation and editing forms. It provides greater simplicity, enabling users to create and manage SIPOC elements without relying on Inter-Process Links (IPLs).
With this method, Modelers can fully build their SIPOC by linking existing EPC objects or by using rich text to represent placeholders for objects that haven’t been created. This approach offers enhanced flexibility and customization, allowing users to tailor their SIPOC to meet the specific needs of their processes.
How to Define SIPOC Using this Method
- When editing or creating a process, select the ‘What is the SIPOC’ accordion.
- Hover over the desired box.
- Click on the
button.
- Add or edit the information.
- You can either input text, or link existing EPC object using the hashtag autocomplete functionality.
- Repeat the previous steps for each box.
- To add a new row, click on the
button.
- To delete a row, click on the
button.
- After saving the form, click on the ‘SIPOC’ accordion in the Details view of the process.
- Hover over a link within the table to display an overview of the linked object.
Need more help with this?
Visit the Support Portal