Background ![]()
For Weatherlink (WL) program versions from v5.8, four distinct interface options became available by which a PC can receive data from various types of WL logger. The options are:
- Serial
- USB
- Modem
- TCP/IP
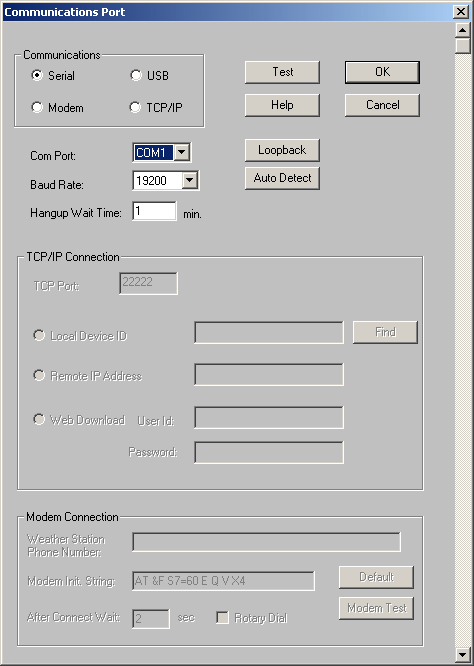
WL classes these interface types as ‘Communications Ports’ (even though a modem isn’t a port in the same sense as Serial or USB) with the required interface type being set in the ‘Communications’ area of the ‘Communications Port’ dialogue – displayed when the ‘Communications Ports’ item on the main WL Setup menu is selected.
These four ‘port’ designations are really just labels for different modes in which data reaches the Weatherlink program itself from the outside world. These labels do not necessarily correspond to the physical interface type of the WL data logger, the main exception being that the USB logger (6510USB) can be set to send its data so that either Serial or USB ‘port’ can be used once the data arrives at the WL program. But the WL software cannot sense – reliably at least – which data type is being sent and an inadvertent mismatch between logger and program settings will often cause logger communications problems.
Setting up the serial (6510SER) or WeatherlinkIP (6555) types of WL logger is, in general, a straightforward process that rarely causes problems, although there is a short section on the TCP/IP options further below. Also, a modem-based data link is rarely used nowadays and is not described further here.
But the other logger type (6510USB) can be configured to use either serial or USB software interfaces and hence it needs setting-up with more care to avoid an interface mismatch. To understand the differences between serial and USB operation of the USB logger in some detail and for instructions about switching between the two modes please see the USB logger modes topic – you may need to read through these notes carefully to fully understand use of the two modes. But in short we recommend the following:
If the Serial option is indeed selected then you will also need to click the Autodetect button in order that the correct virtual Com Port can be identified. Occasionally Autodetect does not succeed at the first attempt and it may be necessary to try again. If a Com Port still cannot be located then you may need to troubleshoot further as described in the Understanding USB logger modes topic. (NB Remember that the logger and its Com Port can only be seen when the logger is connected via USB and the console is powered on.)
TCP/IP options
To be added



Post your comment on this topic.