In the sections of the manual that follow, we will delve into the various forms and workflows of the Audit application.
Generally, the workflows of the Audit application can be divided into four supersets:
- Test Management
This workflow consists of two primary stages: Create Evidence and Create Test.

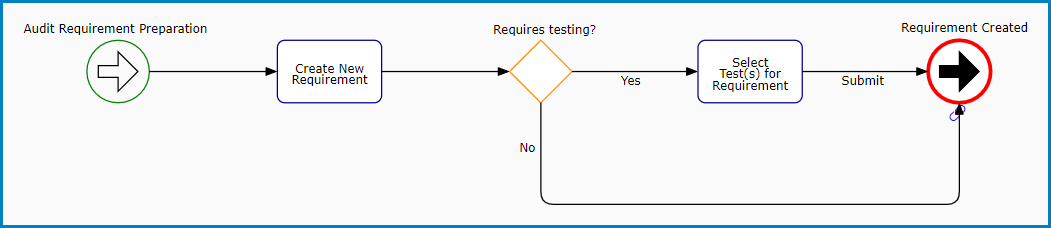
- Requirement Management
This workflow consists of a two primary stages: Create New Requirement and Select Test(s) for Requirement. Both stages are accomplished in the New Requirement form.
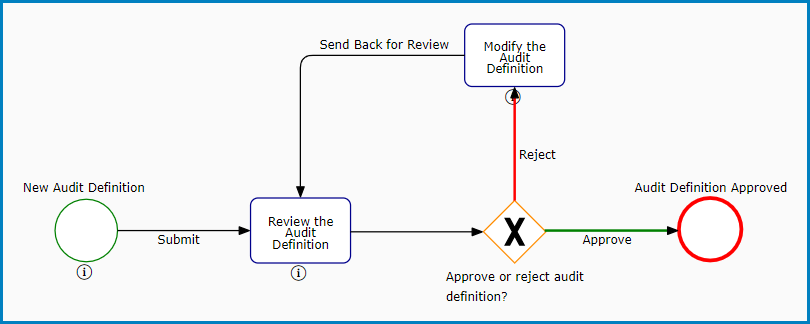
- Audit Definition
This workflow consists of three primary stages: New Audit Definition, Review the Audit Definition, and Modify the Audit Definition.
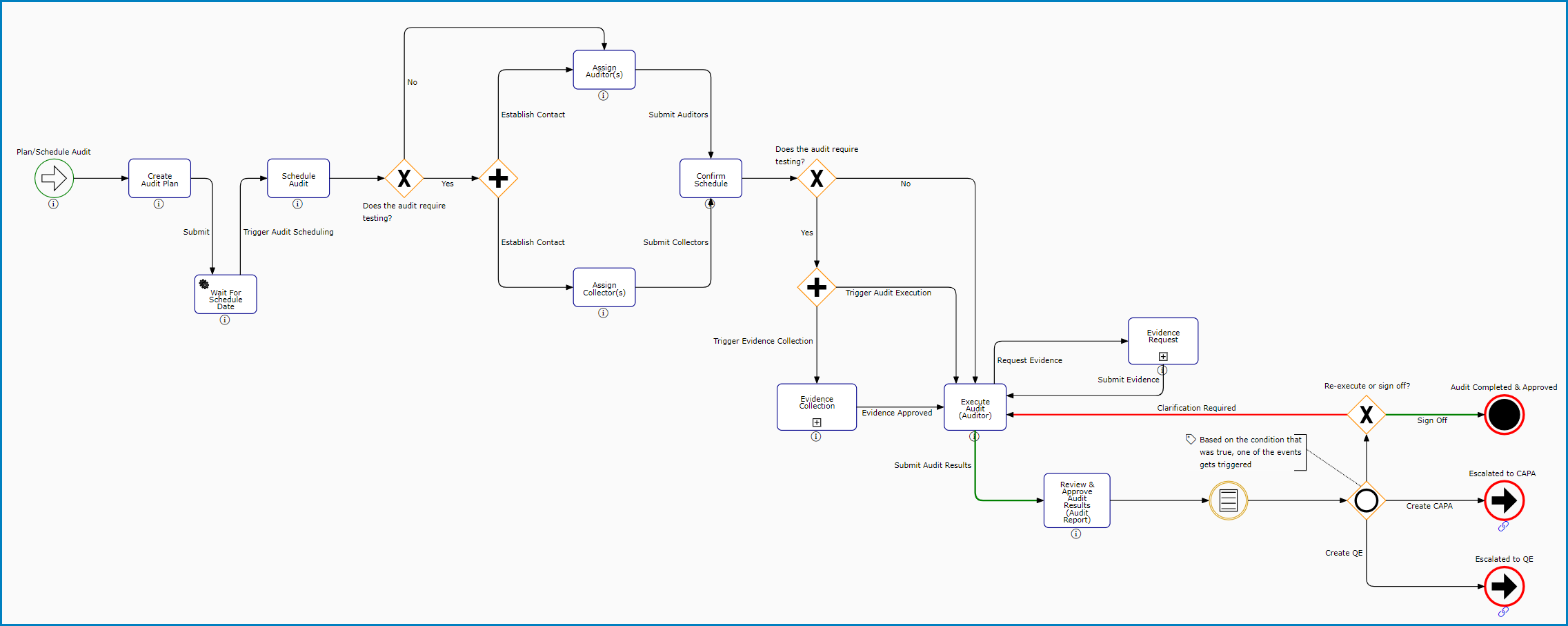
- Audit Planning & Execution
This workflow consists of eight primary stages: New Audit Plan, Schedule Audit, Assign Auditors, Assign Collectors, Confirm Schedule, Evidence Collection, Execute Audit, and Review & Approve Audit Results.
** Although the Assign Collectors task is part of the workflow, it is only issued if an audit requirement is linked to a test.
** Likewise, the Evidence Collection subprocess (described in more detail below) is only included in this workflow if an audit requirement is linked to a test.
The Audit Planning & Execution workflow encompasses two other workflows:
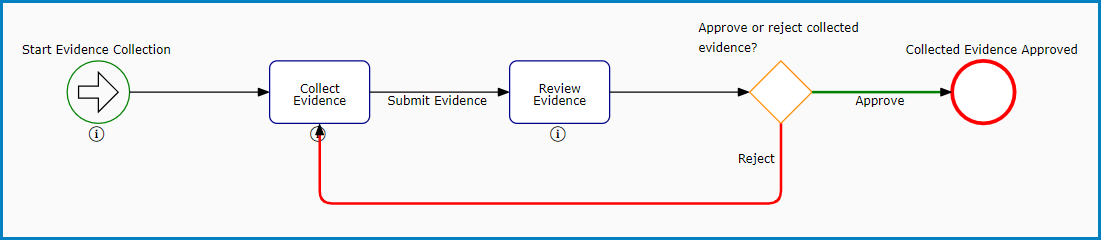
- Evidence Collection
- This workflow is triggered only if an audit requirement is linked to a test—that is, a test with assigned evidence.
- It consists of two primary stages: Collect Evidence and Review Evidence
- Evidence Request
- This workflow is triggered only if an evidence request is issued during the audit execution (through the Validate Requirement form).
- It consists of two primary stages: Request Evidence and Attach Evidence.




Post your comment on this topic.