There is a checkbox on the Look Ahead & Timing tab for Enable Reversing Conveyor Control on Downstream Control Port located at the bottom of the dialog. Reversing conveyor control applies to an entire subnet of modules and the Control Port used for this functionality is always assigned to the Downstream zone of the most Upstream module.
| This checkbox should only be checked on the module that is the most upstream in a subnet | 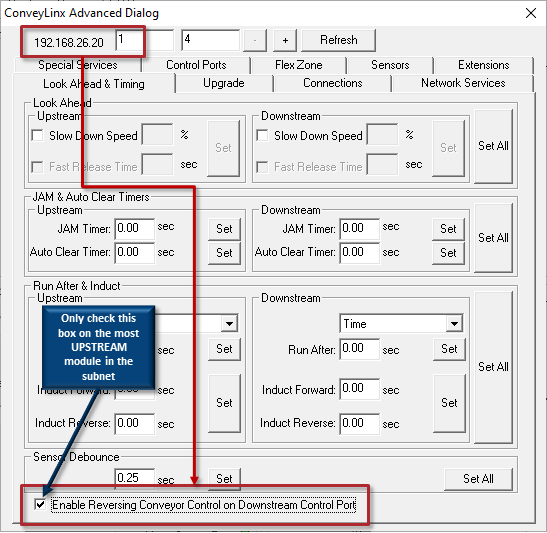 |
Practical Prerequisites for Reversing ZPA Control
- Sensors should be located very close to or in the center of each zone
- Length of all products should be identical or very close to identical
- Induct Forward and Induct Reverse need to be set
Reversing Control Example
Reversing conveyor utilizing hard-wired signal to Control Ports is enabled in EasyRoll as indicated in section Reversing Control on page 91. Figure 61 depicts a simple 8 zone example and indicates which signals on which Control Ports will provide the control. Reversing function applies to all modules in a subnet will work for any number of zones up to the maximum that can be included in a single subnet.
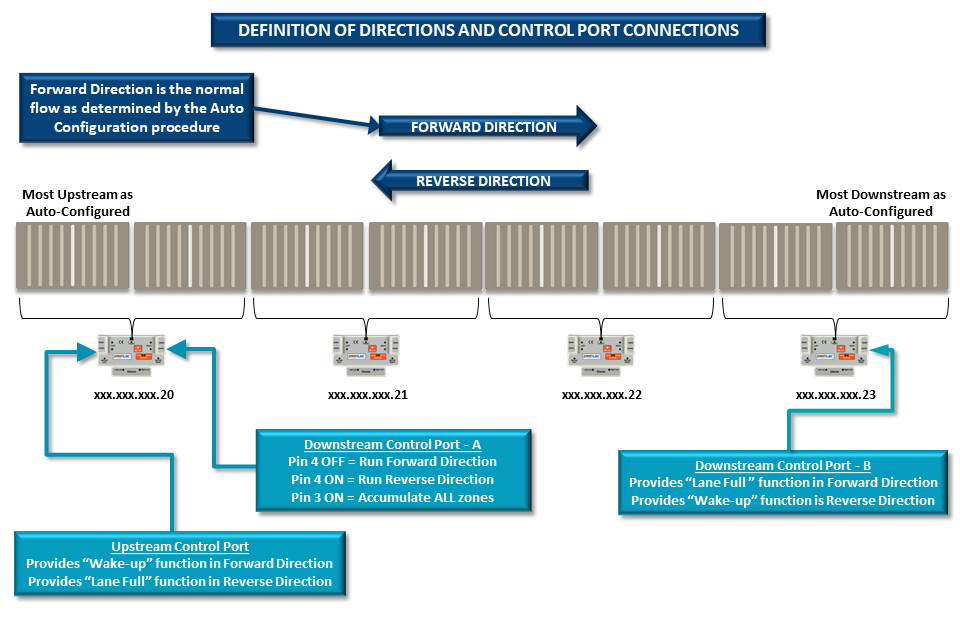
Sequence of Operation
- Forward Direction
- All signals are OFF on Downstream Control Port – A of the xxx.xxx.xxx.20 module
- You can use the Upstream Control Port to wake up the most upstream zone
- You can use the Downstream Control Port-B to hold and accumulate the most downstream zone
- Switching to Reverse Direction
-
Energize Pin 3 on Downstream Control Port-A to cause all zones in the subnet to accumulate
Wait for all zones to stop and accumulate (time value dependent upon zone length and speed – 2 or 3 seconds is typical)
Energize Pin 4 on Downstream Control Port-A to logically switch the direction to Reverse
De-energize Pin 3 on the Downstream Control Port-A to remove accumulation for all zones in subnet to start reversing operation
Note that the Upstream Control Port and Downstream Control Port-B have also reversed their respective functions. Upstream Control Port now provides the Downstream Interlock (lane full) function and the Downstream Control Port-B provides the Upstream Interlock (wake-up) function
- Switching Back to Forward Direction
-
Energize Pin 3 on Downstream Control Port-A to cause all zones in the subnet to accumulate
Wait for all zones to stop and accumulate (time value dependent upon zone length and speed – 2 or 3 seconds is typical)
De-energize Pin 4 on Downstream Control Port-A to logically switch the direction to Forward
De-energize Pin 3 on the Downstream Control Port-A to remove accumulation for all zones in subnet to start forward operation


