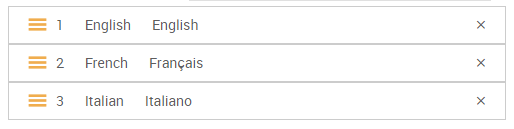
The languages displayed control both the available content when referencing a database and the hierarchy of data query activities.
Adding a content language requires the creation of new tables in MSSQL databases. These tables will feature the translated content (in the new language added) which would largely be a translated replication of the content in existing languages. The tables are required to order and organize the new data available, so upon user request, this data can be retrieved. Thus, adding a new language requires database modification.
The order of the languages represents the hierarchy of data searching activities. This meaning, that when users query content, which is available in multiple languages, the data which will be ultimately featured is prioritized based on the order of the languages.
Data queries will prioritize the content language selected by a user. If content is available in other languages (i.e. not the user’s content language), it will follow the hierarchy displayed in the language list. If content matching the query criteria is only available in 1 language, the query will generate a result in this native language. When queried data does not match the user’s content language, it will be displayed in its native language with a language abbreviation in brackets (e.g. French as [fr], English as [en], Spanish as [sp], etc.).
Please see the following examples with the language order below:
| E.g. | User Content Language | Queried Object Available Languages | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | English | English | En |
| 2 | English | French | [fr] |
| 3 | English | Italian | [it] |
| 4 | English | English, French | En |
| 5 | English | English, Italian | En |
| 6 | English | French, Italian | [fr] |
| 7 | English | English, French, Italian | En |
| 8 | English | Spanish | N/A |
| 9 | French | English, French | Fr |
| 10 | French | English, Italian | [en] |
Haben Sie noch weitere Fragen?
Visit the Support Portal