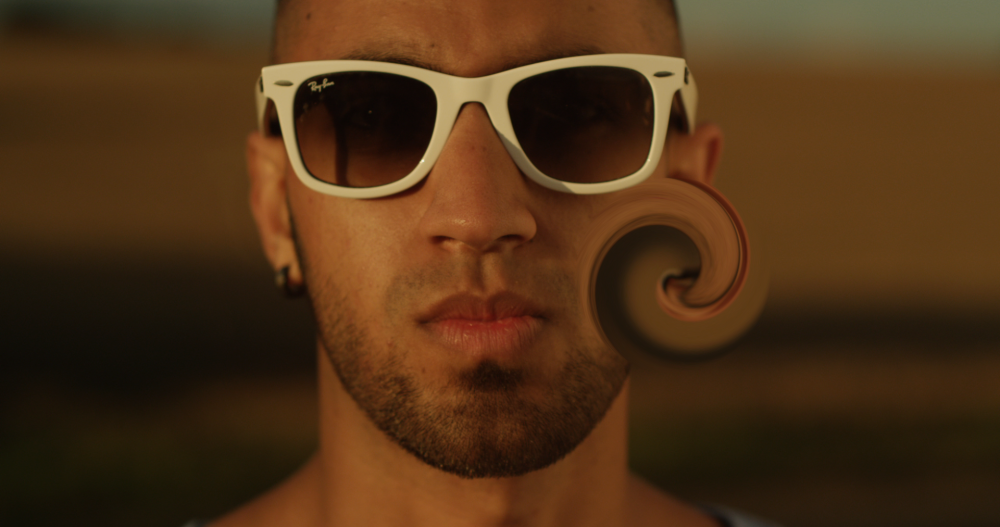
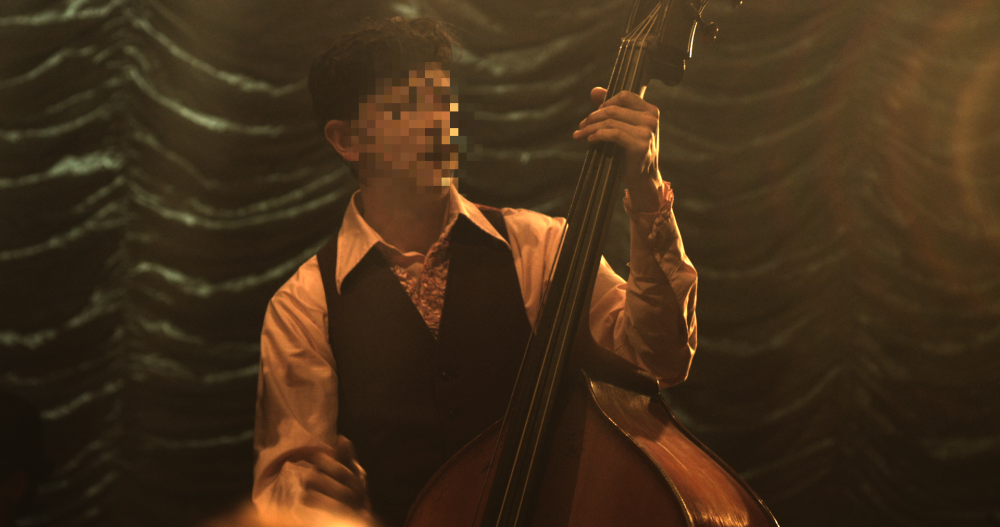
The Distort effects are used to change the shape and behaviour of a layer.
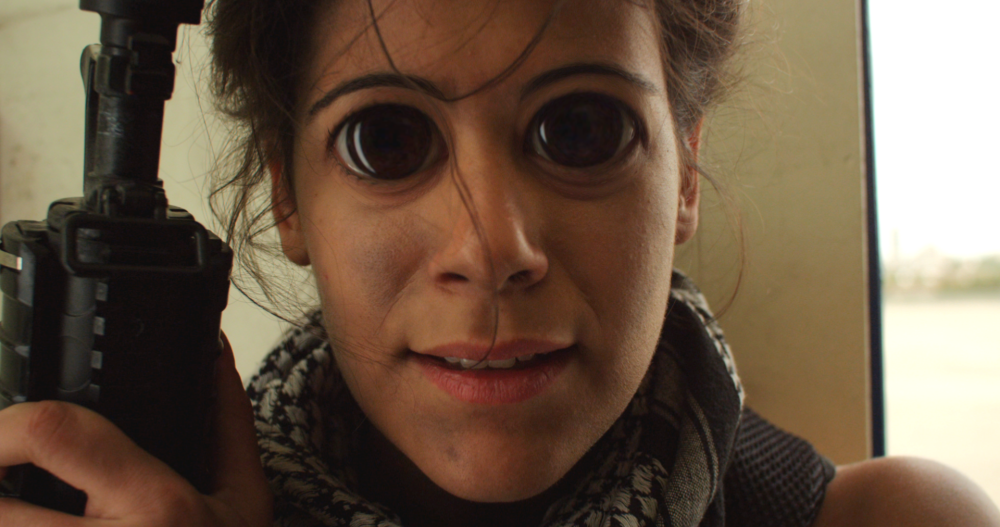
Bulge
Creates the illusion of a bulging shape pushing through the layer.
You can choose from multiple shapes and adjust the size and shape of the bulge.
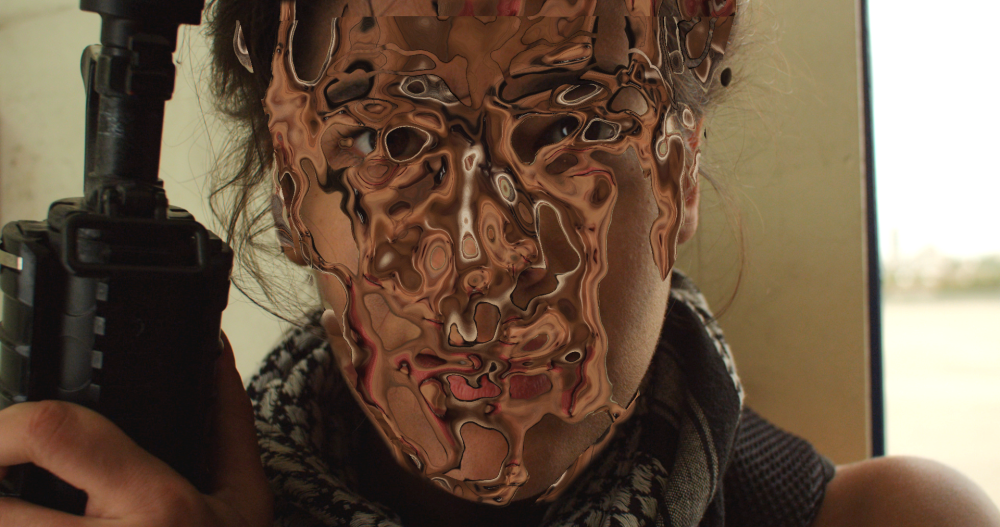
Chromenator
Creates the appearance of liquid metal.
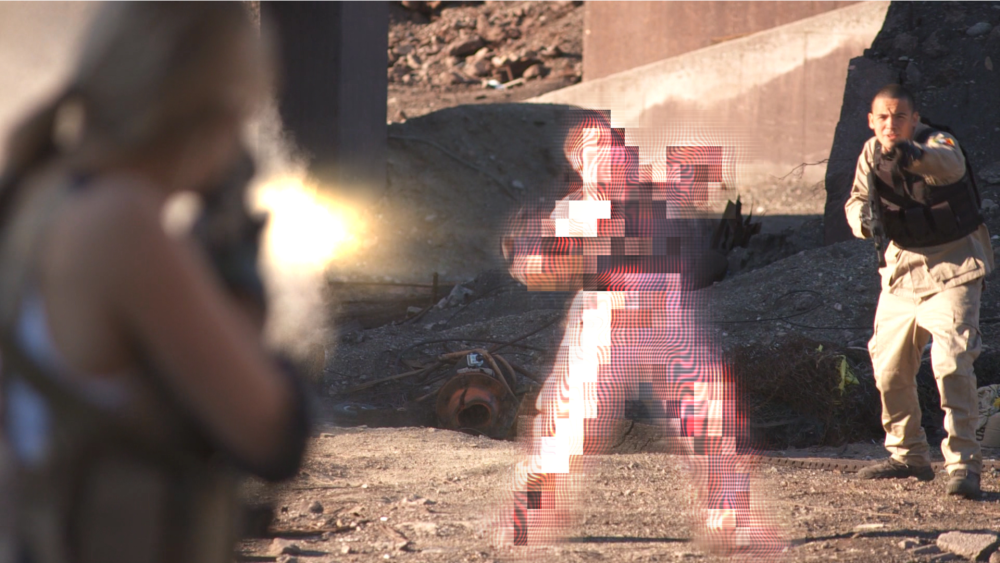
Derez (VGHS)
Custom-built for Freddie Wong’s Video Game High School web series. Creates a digital glitching appearance.
Displacement
Shifts the pixels in particular directions according to the displacement source. This can create excellent invisibility and other distortion effects.
You can select the source layer and source channels, plus adjust the strength of the displacement.
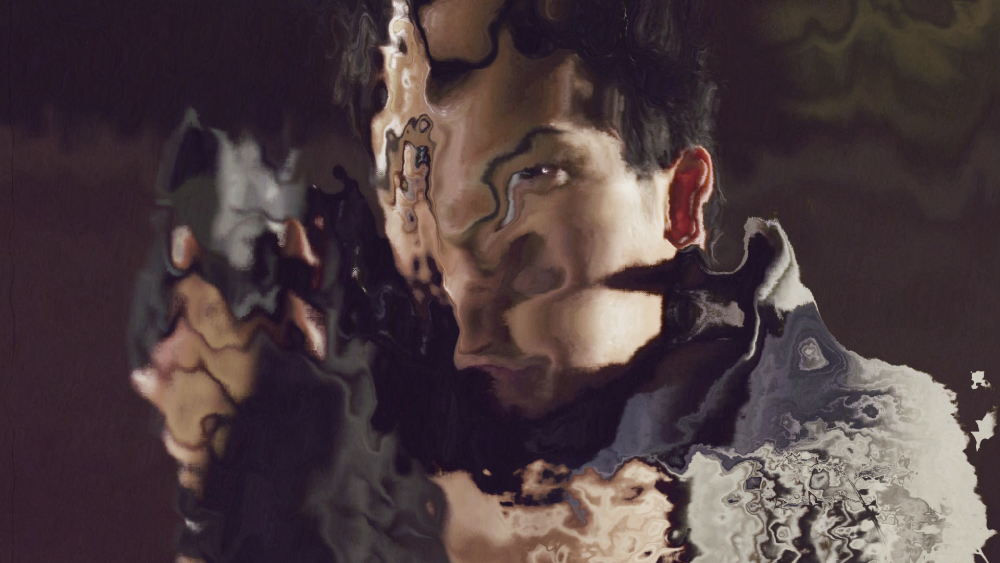

Energy Distortion

Distorts your footage based on a procedurally generated fractal pattern. You can adjust the appearance of the distortion using the controls.
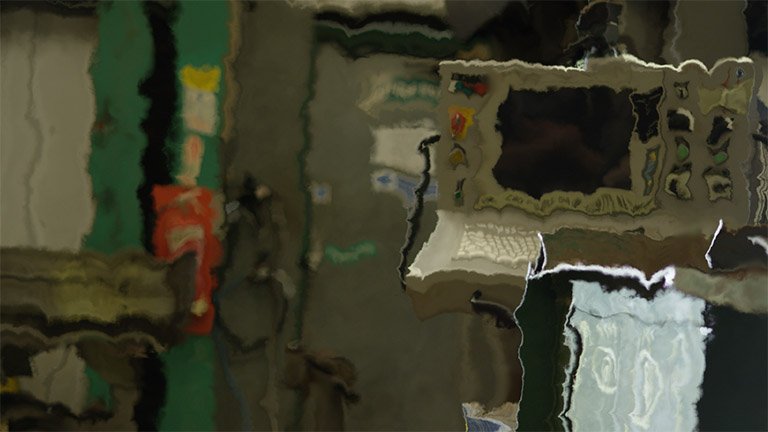

- Distortion: Adjusts the intensity of the distortion applied to the layer.
- Scale: Sets the scale of the distortion
- Diffusion Bias: Set the amount of the image that is affected by diffusion blurring. Increasing the setting will make the blur more prevalent.
- Diffusion Strength: Sets the strength of the blur in the areas affected by diffusion
- Distortion Rotation: Sets the angle in which the distortion is applied.
- Distort Single Axis: Enabling this option applies the distortion in a single direction. The specific angle used can be set with the Distortion Rotation setting above.
Animation
By default the Energy Distortion is animated. You can set the details of the movement within the effect here.
- Wind Direction: Sets the direction of the movement
- Wind Speed: Sets the speed of the movement along the axis determined in the Wind Direction, by altering the position of the noise. Higher values will create more movement in the distortion.
- Noise Speed: Sets the speed of the movement of the fractal noise the distortion is based on. This speed alters the shape of the noise, while the Wind Speed property affects its position.
Noise
- Seed: Acts as a randomizer for the shape of the noise. Each seed value sets a unique starting shape for the procedurally generated noise.
- Interpolation: Provides options for how the noise is interpolated. Linear Interpolation uses the simplest path to connect points in the rectilinear grid the effect is based on. Cubic interpolation uses smoother paths to interpolate the grid. Neither option is better than the other, they just provide different options for the effect.
Transform
Multiple layers of fractal noise are combined to create the final noise that the distortion is based on. The Transform controls adjust the primary noise, while the Sub Settings alter the sub levels of noise that add detail to the distortion.
- Position: Sets the position of the primary fractal noise the distortion is based on.
- Use Layer: You can select another layer on your timeline, to parent the position of the distortion to that layer
- Rotation: Sets the rotation of the primary fractal noise
- Axis Scale X: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the X axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion horizontally.
- Axis Scale Y: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the Y axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion vertically.
Sub Settings
- Sub Levels: Sets the number of sub levels that are used to calculate the distortion. Higher levels create greater detail in the distortion.
- Influence: Controls the intensity with which the sub levels alter the primary noise.
- Scale: Sets the scale of the sub levels, thus impacting the size of the detail added by the additional sub levels.
- Rotation: Alters the angle of the sub levels which are laid over the primary noise.
- Offset: Sets the position of the sub levels in relation to the primary noise position.
- Center Subscale: Enabling this option links the center of all subscale layers, so they stay aligned when offset using the above control.
Fluid Distortion

Distorts your footage based on a procedurally generated fractal pattern. You can adjust the appearance of the distortion using the controls.
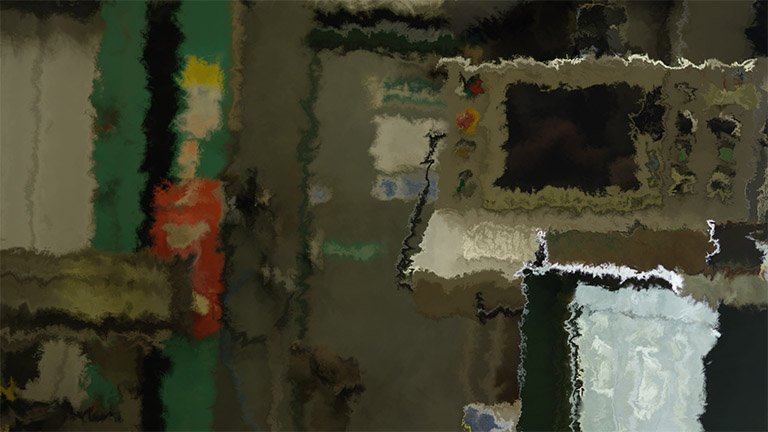

- Distortion: Adjusts the intensity of the distortion applied to the layer.
- Scale: Sets the scale of the distortion
- Diffusion Bias: Set the amount of the image that is affected by diffusion blurring. Increasing the setting will make the blur more prevalent.
- Diffusion Strength: Sets the strength of the blur in the areas affected by diffusion
- Distortion Rotation: Sets the angle in which the distortion is applied.
- Distort Single Axis: Enabling this option applies the distortion in a single direction. The specific angle used can be set with the Distortion Rotation setting above.
Animation
By default the Fluid Distortion is animated. You can set the details of the movement within the effect here.
- Wind Direction: Sets the direction of the movement
- Wind Speed: Sets the speed of the movement along the axis determined in the Wind Direction, by altering the position of the noise. Higher values will create more movement in the distortion.
- Noise Speed: Sets the speed of the movement of the fractal noise the distortion is based on. This speed alters the shape of the noise, while the Wind Speed property affects its position.
Noise
- Seed: Acts as a randomizer for the shape of the noise. Each seed value sets a unique starting shape for the procedurally generated noise.
- Interpolation: Provides options for how the noise is interpolated. Linear Interpolation uses the simplest path to connect points in the rectilinear grid the effect is based on. Cubic interpolation uses smoother paths to interpolate the grid. Neither option is better than the other, they just provide different options for the effect.
Transform
Multiple layers of fractal noise are combined to create the final noise that the distortion is based on. The Transform controls adjust the primary noise, while the Sub Settings alter the sub levels of noise that add detail to the distortion.
- Position: Sets the position of the primary fractal noise the distortion is based on.
- Use Layer: You can select another layer on your timeline, to parent the position of the distortion to that layer
- Rotation: Sets the rotation of the primary fractal noise
- Axis Scale X: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the X axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion horizontally.
- Axis Scale Y: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the Y axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion vertically.
Sub Settings
- Sub Levels: Sets the number of sub levels that are used to calculate the distortion. Higher levels create greater detail in the distortion.
- Influence: Controls the intensity with which the sub levels alter the primary noise.
- Scale: Sets the scale of the sub levels, thus impacting the size of the detail added by the additional sub levels.
- Rotation: Alters the angle of the sub levels which are laid over the primary noise.
- Offset: Sets the position of the sub levels in relation to the primary noise position.
- Center Subscale: Enabling this option links the center of all subscale layers, so they stay aligned when offset using the above control.
Heat Distortion
Applies automatic heat distortion with built-in displacement and diffusion. The behavior can be adjusted for faster or slower movement.
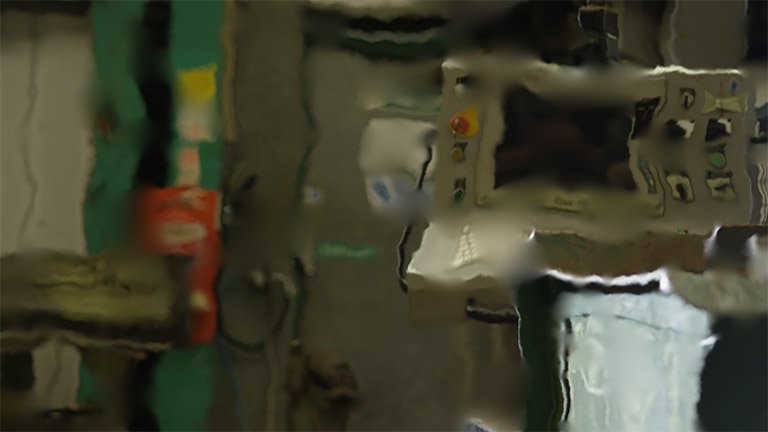

- Scale: Sets the scale of the distortion
- Distortion: Adjusts the intensity of the distortion applied to the layer.
- Diffusion Bias: Set the amount of the image that is affected by diffusion blurring. Increasing the setting will make the blur more prevalent.
- Diffusion Strength: Sets the strength of the blur in the areas affected by diffusion
- Distortion Rotation: Sets the angle in which the distortion is applied.
- Distort Single Axis: Enabling this option applies the distortion in a single direction. The specific angle used can be set with the Distortion Rotation setting above.
Animation
By default the Energy Distortion is animated. You can set the details of the movement within the effect here.
- Wind Direction: Sets the direction of the movement
- Wind Speed: Sets the speed of the movement along the axis determined in the Wind Direction, by altering the position of the noise. Higher values will create more movement in the distortion.
- Noise Speed: Sets the speed of the movement of the fractal noise the distortion is based on. This speed alters the shape of the noise, while the Wind Speed property affects its position.
Noise
- Seed: Acts as a randomizer for the shape of the noise. Each seed value sets a unique starting shape for the procedurally generated noise.
- Interpolation: Provides options for how the noise is interpolated. Linear Interpolation uses the simplest path to connect points in the rectilinear grid the effect is based on. Cubic interpolation uses smoother paths to interpolate the grid. Neither option is better than the other, they just provide different options for the effect.
Transform
Multiple layers of fractal noise are combined to create the final noise that the distortion is based on. The Transform controls adjust the primary noise, while the Sub Settings alter the sub levels of noise that add detail to the distortion.
- Position: Sets the position of the primary fractal noise the distortion is based on.
- Use Layer: You can select another layer on your timeline, to parent the position of the distortion to that layer
- Rotation: Sets the rotation of the primary fractal noise
- Axis Scale X: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the X axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion horizontally.
- Axis Scale Y: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the Y axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion vertically.
Sub Settings
- Sub Levels: Sets the number of sub levels that are used to calculate the distortion. Higher levels create greater detail in the distortion.
- Influence: Controls the intensity with which the sub levels alter the primary noise.
- Scale: Sets the scale of the sub levels, thus impacting the size of the detail added by the additional sub levels.
- Rotation: Alters the angle of the sub levels which are laid over the primary noise.
- Offset: Sets the position of the sub levels in relation to the primary noise position.
- Center Subscale: Enabling this option links the center of all subscale layers, so they stay aligned when offset using the above control.
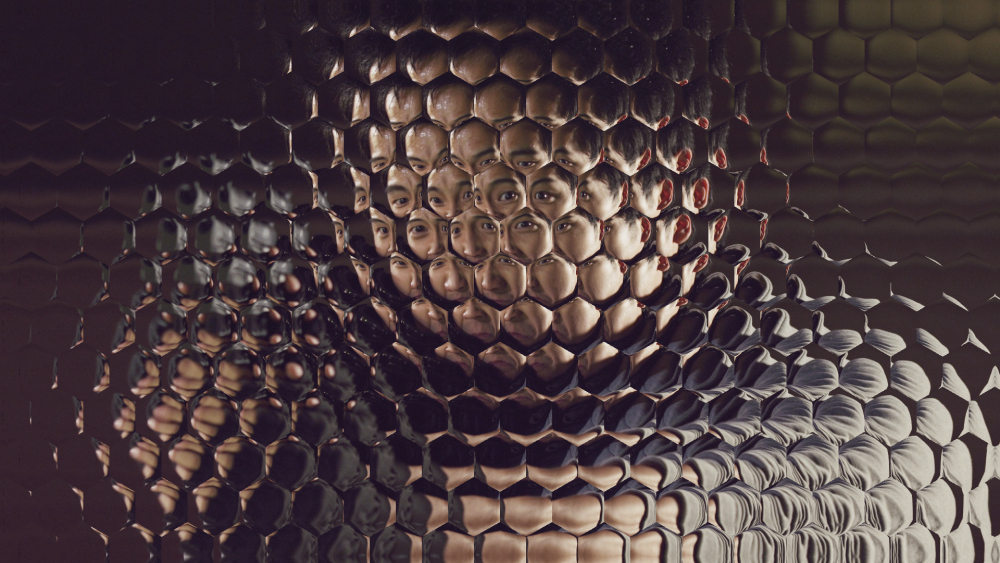
Insect Vision
Creates the tiled appearance of a multi-faceted insect eye.
Magnify
Zooms in on a specific area of the layer. The shape, size and position of the magnification can all be changed.
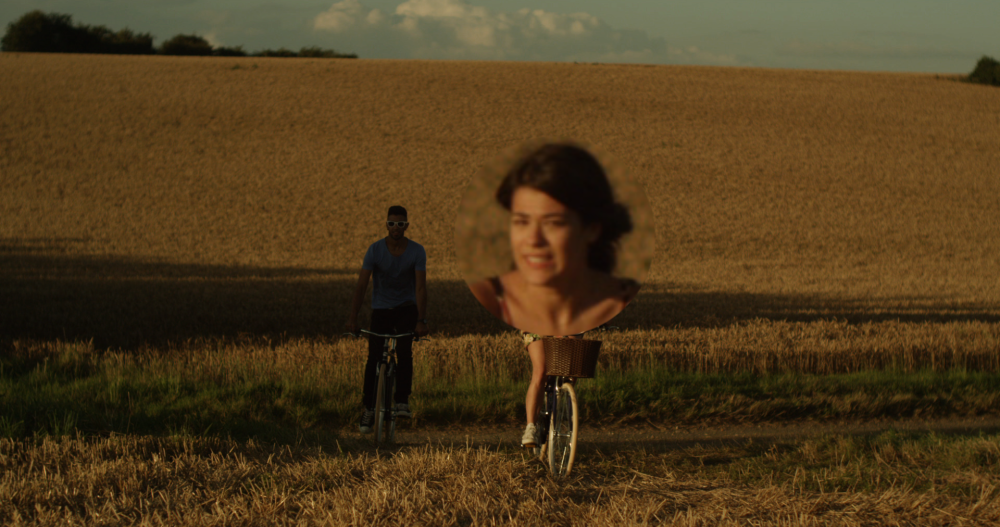

Mosaic
Creates a tiled, mosaic appearance by reducing the number of distinct pixels in the layer.
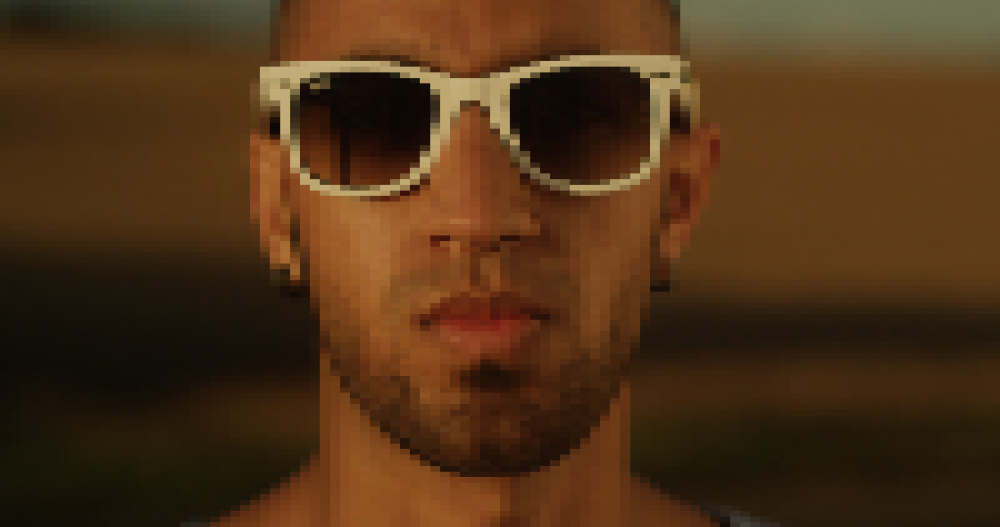

Puppet

The Puppet tool allows you to set up specific control points within your layer, then animate the position of each point to move or distort the layer’s contents. After adding the Puppet effect to your layer, Click in the Viewer to add new control points. A new control point will be added at each location you click. Drag any existing point to a new location to distort the image beneath it. If you wish to reposition a point without distorting the image, hold Shift while you drag the point. While shift is help, the mesh that is used to generate the distortion will be visible, and points can be repositioned without altering the distortion.
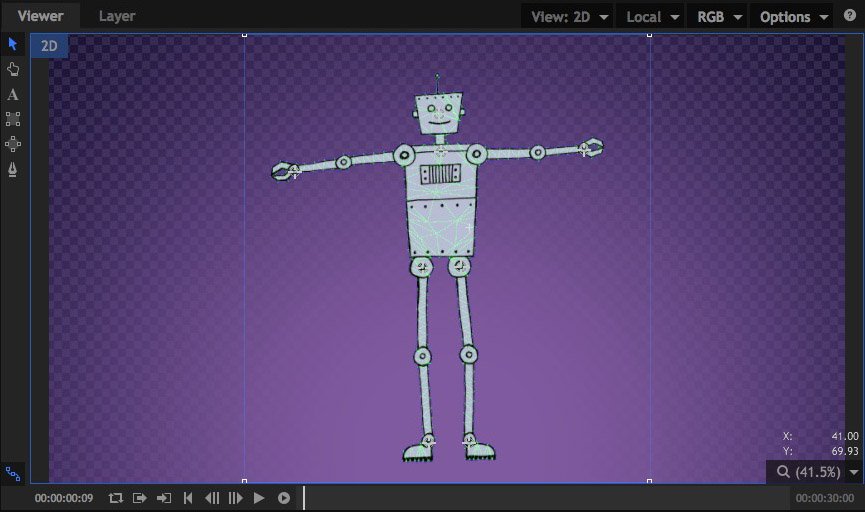
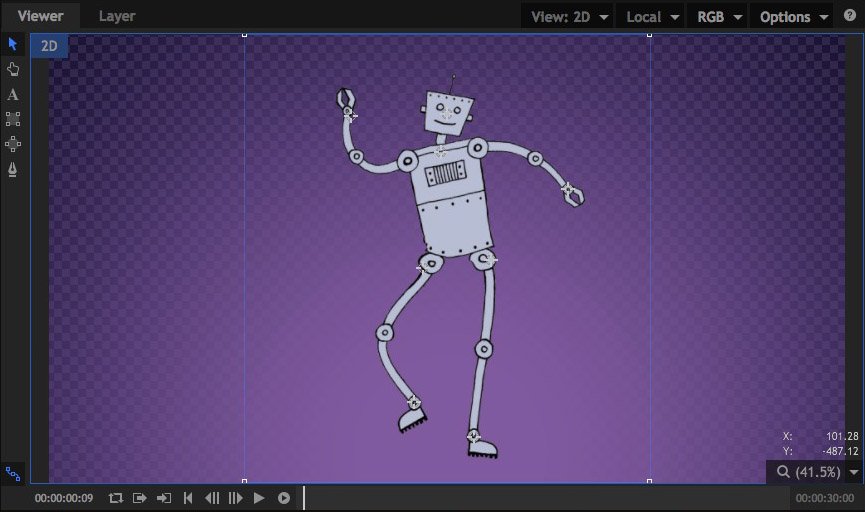
- Mode: The Mode changes automatically as you edit the effect in the Viewer. If you want to manually force a specific mode, you can do so here.
- Animate: In Animate Mode the control points are pined to the layer, and moving any control point will distort the layer accordingly. Note that keyframing must still be enabled for individual control point properties in order to change the values over time.
- Edit: In Edit mode you can add points and change the position of existing points without affecting the source layer. The mesh is overlaid onto your image when Edit mode is active.
When Edit mode is selected, some additional controls appear, which allow you to fine tune the mesh used to distort the image.
- Expansion: Expands the boundaries of the mesh beyond the borders of the layer. If you get unwanted creasing along the edges of your layer when it is distorted, try increasing the expansion to smooth out the edges.
- Tessellation: Controls the size of the triangles that make up the mesh. Increasing tessellation creates more faces, for smoother curves in the distortion. Increased tessellation may also increase processing time.
- Rigidity Map: You can use a map to add rigidity to certain areas of the layer, and further control how it is distorted.
Control Points
You can create as many control points as necessary within the Puppet tool. Control points are numbered in the order in which they are created, and each control point will have two controls:
- Position: Identifies the exact position of the control point at the current frame, on the X and Y axes.
- Z-Order: Controls the depth order of the points. If your points are moved so that parts of the layer overlap, the Z order determines which point is in front. In overlapping areas, point with higher Z-order values will be rendered in front of points with lower values.
Smoke Distortion

Distorts your footage based on a procedurally generated fractal pattern. You can adjust the appearance of the distortion using the controls.
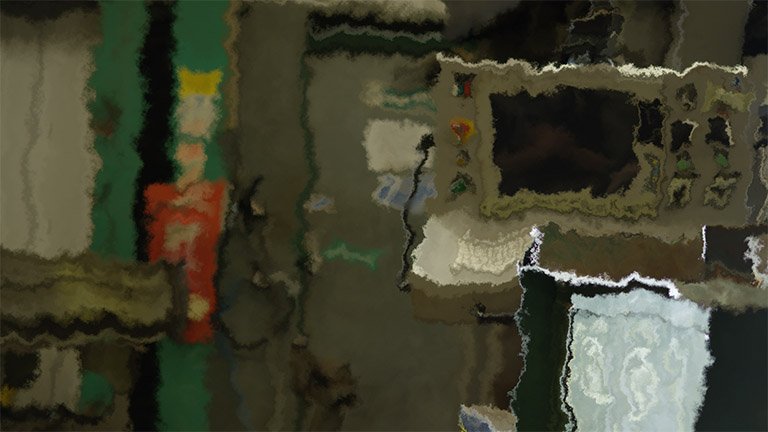

- Distortion: Adjusts the intensity of the distortion applied to the layer.
- Scale: Sets the scale of the distortion
- Diffusion Bias: Set the amount of the image that is affected by diffusion blurring. Increasing the setting will make the blur more prevalent.
- Diffusion Strength: Sets the strength of the blur in the areas affected by diffusion
- Distortion Rotation: Sets the angle in which the distortion is applied.
- Distort Single Axis: Enabling this option applies the distortion in a single direction. The specific angle used can be set with the Distortion Rotation setting above.
Animation
By default the Energy Distortion is animated. You can set the details of the movement within the effect here.
- Wind Direction: Sets the direction of the movement
- Wind Speed: Sets the speed of the movement along the axis determined in the Wind Direction, by altering the position of the noise. Higher values will create more movement in the distortion.
- Noise Speed: Sets the speed of the movement of the fractal noise the distortion is based on. This speed alters the shape of the noise, while the Wind Speed property affects its position.
Noise
- Seed: Acts as a randomizer for the shape of the noise. Each seed value sets a unique starting shape for the procedurally generated noise.
- Interpolation: Provides options for how the noise is interpolated. Linear Interpolation uses the simplest path to connect points in the rectilinear grid the effect is based on. Cubic interpolation uses smoother paths to interpolate the grid. Neither option is better than the other, they just provide different options for the effect.
Transform
Multiple layers of fractal noise are combined to create the final noise that the distortion is based on. The Transform controls adjust the primary noise, while the Sub Settings alter the sub levels of noise that add detail to the distortion.
- Position: Sets the position of the primary fractal noise the distortion is based on.
- Use Layer: You can select another layer on your timeline, to parent the position of the distortion to that layer
- Rotation: Sets the rotation of the primary fractal noise
- Axis Scale X: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the X axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion horizontally.
- Axis Scale Y: Alters the aspect ratio of the primary fractal noise by changing its scale along the Y axis. Higher values will stretch the distortion vertically.
Sub Settings
- Sub Levels: Sets the number of sub levels that are used to calculate the distortion. Higher levels create greater detail in the distortion.
- Influence: Controls the intensity with which the sub levels alter the primary noise.
- Scale: Sets the scale of the sub levels, thus impacting the size of the detail added by the additional sub levels.
- Rotation: Alters the angle of the sub levels which are laid over the primary noise.
- Offset: Sets the position of the sub levels in relation to the primary noise position.
- Center Subscale: Enabling this option links the center of all subscale layers, so they stay aligned when offset using the above control.
Twirl
Twists the layer around the effect’s center point.
Waves
Creates a corrugated effect. You can also choose another layer as the displacement source and alter the lighting on the bright and dark sides of the wave.
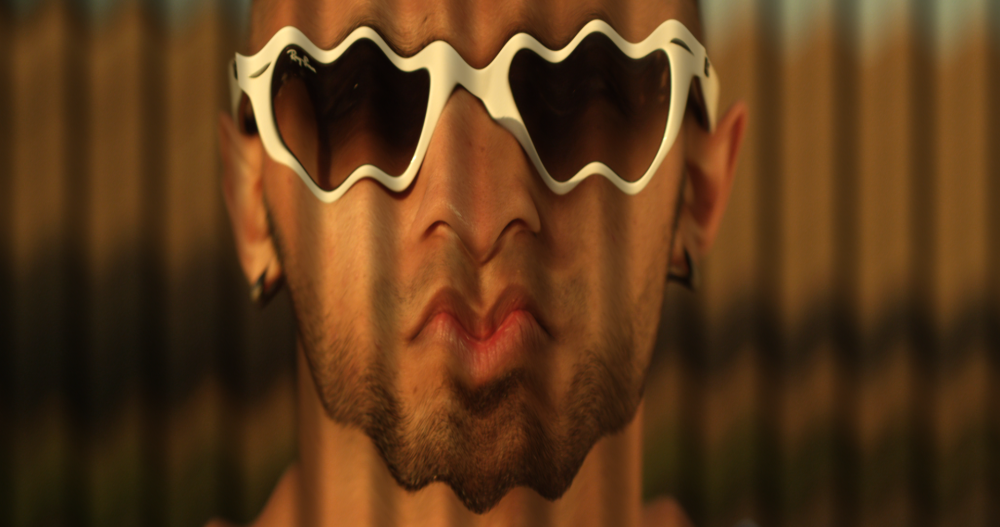

Witness protection
This is a quick way to obscure an item within a shot, such as a face, number plate or product logo. You can choose between blur or pixelate styles.






