Improving Immune Receptor Profiling Through the Use of Validation Barcodes
To enhance the quantification and accuracy of repertoire profiling, we have developed a novel approach employing Validation Barcodes (VBCs). These consist of a redundant set of eight TCR/BCR reverse gene-specific primers (GSPs), each tagged with a unique six-nucleotide barcode for both AIR-RNA and AIR-DNA assays. The VBCs are incorporated into cDNA/DNA during primer extension to create internal replicates, which are then amplified during PCR. The subsequent amplification steps yield eight replicate NGS libraries, each labeled with a distinct Validation Barcode.
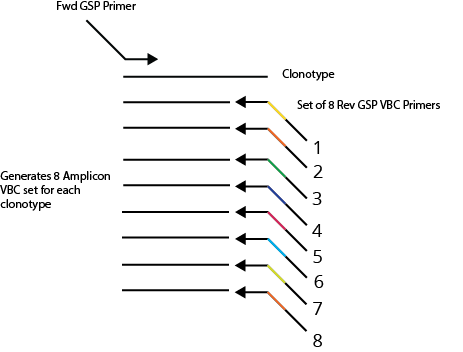
Advantages of the VBC Replicate Approach
Millions of Random Tags vs. Internal Barcoded Replicates
The commonly used Unique Molecular Identifier (UMIs) approach incorporates specific uniquely tagged sequences into each DNA or RNA molecule using primer extension or adaptor ligation before the amplification step. To achieve specific labeling of each template molecule, the number of tags incorporated in primers or adaptors must significantly exceed (usually at least 5-fold) the number of sample template molecules. To achieve this high complexity, the UMI tags are not specific barcode sequences but are designed as random sequences of all four A, G, C, and T nucleotides that are typically at least 10+ nucleotides in length. Using primers with random UMIs could significantly reduce the performance of PCR due to secondary structure and non-specific reaction with non-target molecules (e.g., primer dimers).
In contrast, with Cellecta’s VBCs technology all template molecules present in the sample are labeled with the set of specific barcode sequences (e.g., eight six-nucleotide barcodes). Further, each VBC has been designed to minimize secondary structures and non-specific binding with other primers, and are significantly different from each other (with a Hamming distance of at least 3). As a result, primers with VBCs provide a better yield of correctly amplified genes with less background than primers with UMIs as shown in Figure below.
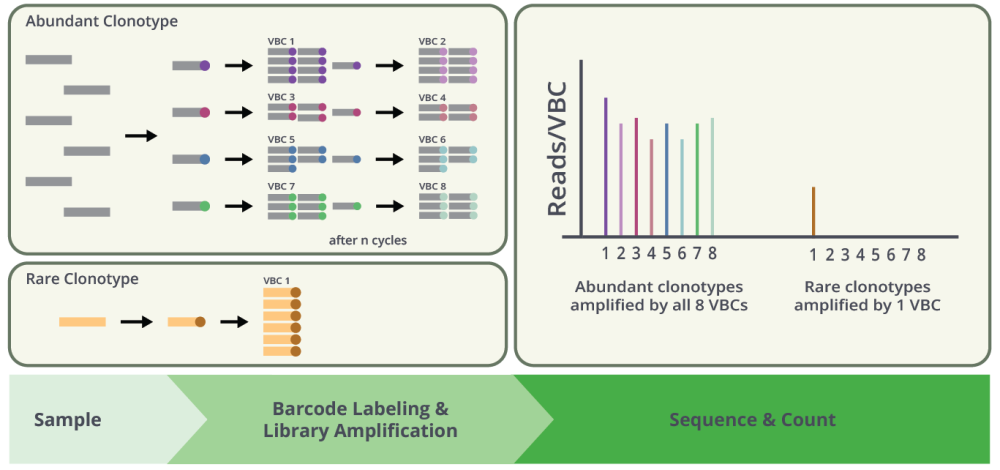
Quantitation and Error Correction of Receptor Clonotypes
UMI labeling enables estimation of the number of molecules of each receptor clonotype present in the original biological sample based on the number of clonotype-specific unique UMI sequences identified in the final amplified reaction by NGS. Also, it provides an approach to correct mutation errors introduced during amplification and NGS steps based on analysis of NGS read number per UMI distribution. UMI-labeled sequences with reading numbers lower than the estimated threshold are mutated sequences whereas those with higher reads are correct sequences. However, because UMI is a random sequence, deletions introduced during oligo synthesis or mutations in the amplification and NGS steps are difficult to correct and compromise the accuracy of calculating the number of template molecules associated with any specific clonotype.
In contrast, with VBC technology, any medium-high represented receptor clonotypes in the sample will be labeled with several (up to eight) VBC sequences. Therefore, VBCs are working as internal replicates which very accurately quantify an abundance level of medium-high abundant receptor clonotypes. On the other hand, low abundant clonotypes present in the sample as single template molecules are easily identified since they are only labeled with a single VBC barcode. The read numbers of the single-VBC labeled rare clonotypes amplified from single molecules provide a more definitive approach to normalize the NGS read numbers for the number of template molecules and enable accurate calculation of the number of template molecules for all receptor clonotypes present in biological samples as shown in graphic below.
Improved Performance of AIR-VBC technology
Cellecta’s VBC technology based on internal replicate measurement offers a unique approach to generating accurate, quantitative receptor repertoire profiling data for biologically important clonotypes that are present in biological samples at medium-high abundance levels. Furthermore, the barcoding strategy using VBCs enables calculation of the ratio of NGS read counts to a number of template molecules for each clonotype while more precisely excluding mutated sequences from follow-up analysis.

Need more help with this?
Contact Us

