In v11.4.0 of the HITRUST CSF and later, a new HITRUST Security for AI Systems compliance factor will be made available. This factor can be optionally added to HITRUST e1, i1, and r2 readiness and validated assessments which include within the scope of the assessment an IT platform that leverages an AI model.
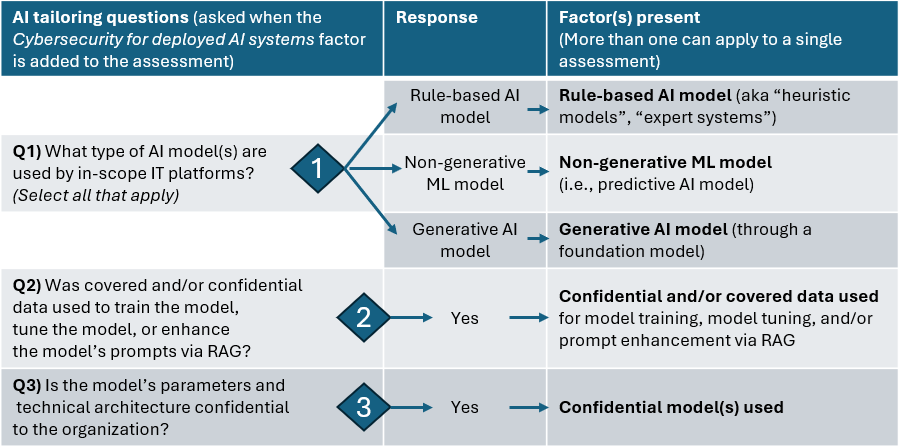
When the HITRUST Security for AI Systems compliance factor is added to a HITRUST assessment, three additional tailoring questions will be asked:
The following table includes information about each potential response to question 1. These will be presented as checkboxes in MyCSF (not as radio buttons), allowing many to be selected for a single assessment (as is needed if the assessment’s in-scope IT platforms leverage more than one type of AI model).
| Factor / response | Description | Examples and behavior considerations | Impact on the assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule-based AI model (aka “heuristic models”, “traditional AI, “expert systems”, “symbolic AI” or “classical AI”) | Rule-based systems rely on expert software written using rules. These systems employ human expertise in solving complex problems by reasoning with knowledge. Instead of procedural code, knowledge is expressed using If-Then/Else rules. | HITRUST AIE, AML systems for financial institutions, prescription dosing calculators | Adds 27 “base AI security” HITRUST CSF requirement statements |
| Predictive AI model (i.e., a non-generative machine learning model) | These are traditional, structured data machine learning models used to make inferences such as predictions or classifications, typically trained on an organization’s enterprise tabular data. These models extract insights from historical data to make accurate predictions about the most likely upcoming event, result or trend. In this context, a prediction is does not necessarily refer to predicting something in the future. Predictions can refer to various kinds of data analysis or production applied to new data or historical data (including translating text, creating synthetic images or diagnosing a previous power failure). | scikit-learn, XGBoost, PyTorch and Hugging Face transformer models | Adds 27 “base AI security” requirements + 9 additional requirements = 36 added requirements |
| Generative AI model (through a foundation model) | Generative AI (gen AI) is artificial intelligence that responds to a user’s prompt or request with generated original content, such as audio, images, software code, text or video. Most generative AI models start with a foundation model, a type of deep learning model that “learns” to generate statistically probable outputs when prompted. Large language models (LLMs) and small language models (SLMs) are common foundation models for text generation, but other foundation models exist for different types of content generation. | OpenAI ChatGPT, Anthropic Claude, Meta LLAMA, Google Gemma, Amazon Titan, Microsoft Phi | Adds 27 “base AI security” requirements + 9 additional requirements associated with predAI + 5 additional Gen-AI only requirements = 41 added requirements |
The following table describes question 2 and 3. These will be presented as radio buttons in MyCSF, allowing only one answer. If the assessment’s in-scope IT platforms leverage many models, assessed entities should use a high-water mark approach to answering these two questions. For example, if one in-scope model is open source and the other model is closed source and confidential to the organization, question 3 should be answered affirmatively.
| Question no. | Question | Description | Impact on the assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Was confidential and/or covered data used to train the model, tune the model, or enhance the model’s prompts via RAG? | AI models often require large volumes of data to train and tune. This data, as well as the sources of organizational data used for prompt enhancement through retrieval augmented generation (RAG), is very often confidential and/or covered information. When this is true, additional protections must be in place to prevent the theft and leakage of this data through the AI system. Per the per the HITRUST Glossary:
|
Adds 3 requirements if true, which deal with protections (encryption, data minimization, added model robustness) |
| 3 | Are the model’s architecture and parameters confidential to the organization? | The training of an AI model can be a significant undertaking. While some AI models are open source, the inner workings of many AI models and the models themselves represent valuable intellectual property for the organization that created them. When this is true, additional protections must be in place to prevent the theft of the model and leakage of model parameters. | Adds 2 requirements if true (encryption, data minimization) |
MyCSF uses the collective responses to these questions to appropriately tailor the HITRUST CSF assessment to the specifics of the organization’s AI deployment context. The following table shows the different requirement statement counts possible based on different combinations of responses to these tailoring questions. Note that this table contemplates only a single model type included in the scope of the assessment. As stated above, more than one IT platform can be included in the scope of a HITRUST CSF assessment which leverages an AI model. When this is true, the assessed entity should select all model types that apply for question 1 and should follow a high-water mark approach to answering questions 2 and 3.
| Q2: Sensitive data used | Q3: Confidential model used? | Requirement count |
|---|---|---|
| Rule-based AI model | ||
| No | No | 27 |
| Yes | No | 27 |
| No | Yes | 27 |
| Yes | Yes | 27 |
| Predictive AI model | ||
| No | No | 36 |
| Yes | No | 38 |
| No | Yes | 38 |
| Yes | 40 | |
| Generative AI model | ||
| No | No | 41 |
| Yes | No | 44 |
| No | Yes | 43 |
| Yes | Yes | 44 |